ADRENALS: HYPERALDOSTERONISM
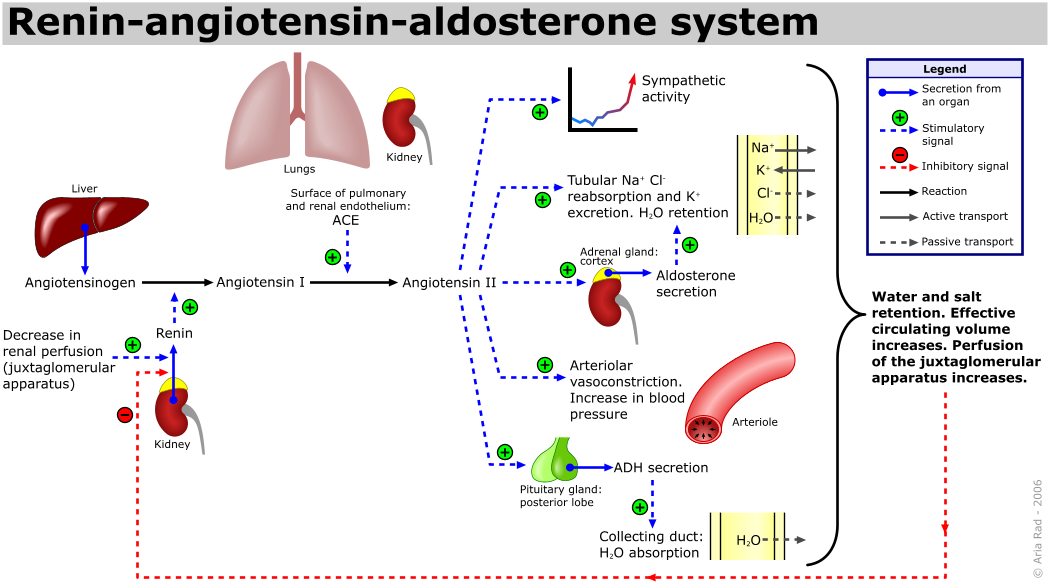
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone-System (RAAS)
- Under normal physiologic conditions, renin release is stimulated by (low-volume, low-salt state):
- Low renal perfusion pressure
- Increased renal sympathetic nervous activity
- Low sodium concentration sensed by the macula densa
- Renin then cleaves angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, which in turn is cleaved by angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) to angiotensin II
- Angiotensin II
- Functions (2):
- Potent vasoconstrictor
- In kidneys, angiotensin II causes vasoconstriction of efferent and afferent arterioles, with stronger effect on efferent arteriole.
- Triggers the release of aldosterone
- Potent vasoconstrictor
- Functions (2):
- Aldosterone
- Produced by:
- Zona glomerulosa of adrenal gland
- Production
- Stimulated by (3):
- Angiotensin II (most potent stimulator)
- Elevated serum potassium and decreased serum sodium
- ACTH (much less potent stimulator)
- The zona glomerulosa is the only region of the adrenal cortex that does not atrophy on pituitary failure
- Inhibited by:
- Atrial natriuretic peptide
- Stimulated by (3):
- Function:
- Increases sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion in the distal nephron.
- The increased sodium reabsorption increases total body volume.
- Increases sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion in the distal nephron.
- Produced by:
Source: Wikipedia
Classification of hyperaldosteronism: primary vs. secondary
- Primary
- Aldosterone secretion is independent of the RAAS
- Renin levels are suppressed
- Can lead hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, alkalosis, fluid depletion or retention, refractory hypertension, cardiac dysfunction and arrhythmias
- Hypernatremia does not occur because sodium reabsorption is accompanied by water uptake, thereby maintaining isotonicity.
- Most patients are normokalemic
- Although hypokalemia has been classically described as a common finding in primary aldosteronism, only 9-37% of newly diagnosed patients are hypokalemic
- Hypertension secondary to hyperaldosteronism is associated with an increased risk of end-organ damage compared with essential hypertension
- Causes (8):
- Bilateral hyperplasia (60%), also referred to as idiopathic hyperplasia;
- Clinically, patients with bilateral adrenal hyperplasia have less severe hypertension and are less likely to be hypokalemic compared with patients with aldosterone-producing adenomas
- Aldosterone-producing adrenal adenoma (35%)
- Unilateral adrenal hyperplasia (2%)
- Aldosterone-producing adrenal cortical carcinoma (<1%)
- Ectopic aldosterone-producing tumour (<1%)
- Familial hyperaldosteronism I (<1%)
- Aldosterone production is mediated by ACTH in familial hyperaldosteronism type I
- Familial hyperaldosteronism II (<1%)
- Familial hyperaldosteronism III (<1%)
- Bilateral hyperplasia (60%), also referred to as idiopathic hyperplasia;
- Aldosterone secretion is independent of the RAAS
- Secondary
- Elevated renin levels are the cause of elevations in aldosterone secretion
- Causes of elevated renin(4):
- Hypovolemia
- Juxtaglomerular cell tumour
- Renal artery stenosis
- Fibromuscular dysplasia
Primary hyperaldosteronism
- Diagnosis and Evaluation
- Indications for primary hyperaldosteronism screening (9):
- Unexplained hypokalemia (spontaneous or diuretic induced)
- Hypertension with hypokalemia
- Adrenal incidentaloma with hypertension
- Resistant hypertension (3 or more oral agents with poor control)
- Early-onset hypertension (<20 years) or stroke (<50 years)
- Severe hypertension (≥160/≥110)
- Whenever considering secondary causes of hypertension (i.e., pheochromocytoma or renovascular disease)
- Evidence of target organ damage disproportionate to degree of hypertension
- Hypertension with family history of primary aldosteronism
- Primary hyperaldosteronism may be unmasked by diuretic-induced hypokalemia. The diagnosis is confirmed if 24-hour urinary aldosterone levels remain elevated after sodium loading (see below). After confirming diagnosis, a CT scan is done to localized the tumour.
- Labs
- Aldosterone-to-renin ratio (ARR)
- Used to screen for primary hyperaldosteronism.
- Involves measuring a morning (between 8-10 AM) plasma aldosterone concentration (PAC) and plasma renin activity (PRA).
- An ARR of > 20 (some suggest > 30) along with a concomitant aldosterone concentration > 15 ng/mL is indicative of hyperaldosteronism; standard thresholds have not been established due to laboratory variability.
- Before screening is initiated, hypokalemia should be corrected and all contraindicated medications discontinued.
- Although patients can continue the majority of anti-hypertensive agents during screening, potassium-sparing diuretics such as amiloride or triamterene, and especially mineralocorticoid receptor blockers such as spironolactone and eplerenone, alter the RAAS and will affect test results. These medications should be stopped approximately 6 weeks before testing.
- 50-70% of patients with a positive screening test will be diagnosed with primary aldosteronism following confirmatory testing. The majority of confirmatory tests evaluate the suppression of aldosterone after sodium loading.
- The underlying theory behind the sodium loading tests is that loading will decrease plasma renin and aldosterone production in patients without autonomous aldosterone secretion.
- The oral sodium loading test is conducted by administering a high-sodium diet for 3 days, followed by 24-hour urine measurements of aldosterone, sodium, and creatinine.
- The underlying theory behind the sodium loading tests is that loading will decrease plasma renin and aldosterone production in patients without autonomous aldosterone secretion.
- Aldosterone-to-renin ratio (ARR)
- Imaging
- Cross-sectional abdominal imaging should be performed in all patients with primary aldosteronism who are potential surgical candidates.
- Radiographic characteristics of aldosterone-producing adenomas include the presence of a unilateral low-density non-enhancing lesion of < 10 Hounsfield units
- Lateralization of adrenal aldosterone-producing disease cannot be based on CT alone. Patients with confirmed primary aldosteronism should undergo adrenal vein sampling to establish lateralization when adrenalectomy is being considered. Exceptions include:
- Patients <40 years with a clear unilateral adrenal adenoma and normal contralateral adrenal gland on imaging
- Patients suspected of having an ACC
- Lateralization of adrenal aldosterone-producing disease cannot be based on CT alone. Patients with confirmed primary aldosteronism should undergo adrenal vein sampling to establish lateralization when adrenalectomy is being considered. Exceptions include:
- Genetic screening
- Given the rarity of familial primary hyperaldosteronism, genetic screening should not be performed in all patients. However, patients with a family history of primary aldosteronism, early age of onset (<20 years), or with a family history of cerebral vascular accidents at a young age should be considered for genetic testing
- Indications for primary hyperaldosteronism screening (9):
Management
- Role of surgery depends on cause
- Surgically correctable causes of hyperaldosteronism (4)
- Aldosterone-producing adrenal adenoma
- Unilateral adrenal hyperplasia
- Ectopic aldosterone-secreting tumor
- Aldosterone-producing adrenal cortical carcinoma
- Non-correctable by surgery causes of hyperaldosteronism (4)
- Bilateral adrenal hyperplasia
- Familial hyperaldosteronism type I
- Familial hyperaldosteronism type II
- Familial hyperaldosteronism type III
- Surgically correctable causes
- In patients with confirmed lateralizing aldosterone secretion, adrenalectomy should be considered.
- Adrenalectomy Approach
- Given the small size of aldosterone-producing adenomas, the majority of patients are candidates for a laparoscopic adrenalectomy.
- In patients suspected of having hypersecretion of aldosterone associated with ACC, an open procedure may be recommended
- Non-correctable by surgery causes
- Medical treatment of primary aldosteronism in the form of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (spironolactone and eplerenone) is indicated in patients with non-surgically correctable subtypes and those who are not surgical candidates.
- Surgically correctable causes of hyperaldosteronism (4)
Questions
- What is the most potent stimulator of aldosterone secretion? What are other stimulators of aldosterone secretion?
- What is the categorization of causes of hyperaldosteronism? What lab test can be used to differentiate them?
- List 8 causes of primary hyperaldosteronism
- List 9 indications for primary aldosteronism screening?
- Which medications should be held prior to testing for hyperaldosteronism?
- What are the surgically correctable subtypes of hyperaldosteronism? What are the non correctable by surgery subtypes of hyperaldosteronism?
- What laboratory test do the CUA guidelines recommend to rule out primary hyperaldosteronism?
- How is laterality of primary hyperaldosteronism established? When should this not be performed?
- What are medical treatments for the non correctable by surgery subtypes of hyperaldosteronism?
Answers
- What is the most potent stimulator of aldosterone secretion? What are other stimulators of aldosterone secretion?
- Angiotensin II
- ACTH and elevated serum potassium
- What is the categorization of causes of hyperaldosteronism? What lab test can be used to differentiate them?
- Primary vs. secondary
- Plasma aldosterone-renin ratio
- List 8 causes of primary hyperaldosteronism
- Bilateral hyperplasia
- Aldosterone-producing adrenal adenoma
- Unilateral adrenal hyperplasia
- Aldosterone-producing ACC
- Ectopic aldosterone-producing tumour
- Familial hyperaldosteronism I
- Familial hyperaldosteronism II
- Familial hyperaldosteronism III
- List 9 indications for primary aldosteronism screening?
- Which medications should be held prior to testing for hyperaldosteronism?
- What are the surgically correctable subtypes of hyperaldosteronism? What are the non correctable by surgery subtypes of hyperaldosteronism?
- Surgically correctable: aldosterone-producing adrenal adenoma, unilateral adrenal hyperplasia, ectopic aldosterone-secreting tumor, aldosterone-producing adrenal cortical carcinoma
- Not correctable by surgery: bilateral adrenal hyperplasia, familial hyperaldosteronism type I, familial hyperaldosteronism type II, familial hyperaldosteronism type III
- What laboratory test do the CUA guidelines recommend to rule out primary hyperaldosteronism?
- How is laterality of primary hyperaldosteronism established? When should this not be performed?
- Adrenal vein sampling; lateralization cannot be established on imaging alone
- Patients <40 years with a clear unilateral adrenal adenoma and normal contralateral adrenal gland on imaging or patients suspected of having an ACC
- What are medical treatments for the non correctable by surgery subtypes of hyperaldosteronism?
- Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists such as spironolactone and eplerenone
References
- Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Partin AW, Peters CA (eds): CAMPBELL-WALSH UROLOGY, ed 11. Philadelphia, Elsevier, 2015, chap 65
- Daneshvar M, Bratslavsky G. 2019 AUA Update on Pheochromocytoma.