FUNCTIONAL: PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE
Pelvic Organ Prolapse (POP)
- Categorized according to the affected compartment:
- Anterior compartment prolapse: weakness of the anterior vaginal wall often associated with the descent of the bladder (cystocele)
- Posterior compartment prolapse: weakness of the posterior vaginal segment often associated with bulging of the rectum into the vagina (rectocele) but can include the small intestine (enterocele).
- Apical prolapse: descent of the uterus, cervix, (or in the posthysterectomy patient, the vaginal cuff), vaginal vault, and/or the bowel (enterocele) at the top of the vagina
- Enterocele is a true hernia of the intestines into the vaginal wall.
- Prolapse occurs most frequently in the anterior compartment, followed by the posterior compartment, and least commonly in the apex
- Complete uterine prolapse (procidentia) can cause bilateral ureteral obstruction.
- Correction of the prolapse causes relief of the ureteral obstruction.
Normal Pelvic Support Mechanisms
- 3 levels
- Level I: suspends the uterus and upper vagina to the sacrum and lateral pelvic sidewall.
- [Loss of level I support contributes to apical prolapse]
- Level II: includes the paravaginal attachments of the middle third of the vagina laterally to the superior fascia of the levator ani muscle and the arcus tendineus fascia pelvis.
- Loss of level II support contributes to anterior vaginal wall prolapse/cystocele
- Level III: includes the vagina’s lower third attachments with the perineal membrane, levator ani muscles (superficial and deep perineal muscles), and perineal body.
- Loss of level III support anteriorly contributes to urethral mobility
- Loss of level III support posteriorly results in a distal rectocele or perineal descent
Pathophysiology of POP
- Well-established risk factors (3):
- Age
- Obesity
- Parity
- Increasing number of childbirths increases the risk of POP, although the rate of increase slows after the first two deliveries
- Less well-established risk factors (7):
- Race/ethnicity
- More common in Caucasian and Hispanic women when compared with African-American women
- Increasing weight of the vaginally delivered fetus
- Hysterectomy and other pelvic surgery
- Hysterectomy performed for POP is a strong predictor of the need for repeat pelvic floor surgery
- Genetic predisposition
- Smoking
- Chronic constipation
- Menopause/hormonal effects
- Race/ethnicity
Urinary incontinence and POP
- POP can exacerbate storage lower urinary tract symptoms
- Important to identify and manage symptomatic prolapse when evaluating patients with UI
- > 40% of women with SUI will have a significant cystocele
- Procedures for UI [without correction of POP] can exacerbate certain types of POP
- Improvement of storage symptoms can be expected after POP surgery in a significant proportion of patients
- Occult SUI is urethral sphincteric incompetence masked by the presence of high-stage anterior POP.
- Failure to address occult SUI at the time of surgery for POP may lead to more severely symptomatic SUI postoperatively.
- Although POP is generally considered a QoL condition with few medical sequelae, untreated prolapse can become advanced to a point when a woman can develop urinary retention from urethral compression and, rarely, renal failure from ureteral compression.
Diagnosis and evaluation
- History and Physical Exam
- History
- Whether the patient is aware of any prolapse and what, if any, symptomatology and bother the prolapse may be causing.
- Sensation of a vaginal bulge remains the only symptom that is strongly associated with prolapse at or below the hymenal ring
- Other symptoms, including UI and fecal incontinence, voiding and defecation difficulty, and sexual dysfunction, frequently coexist with POP, but they correlate weakly with the severity or site of POP
- Disorders of defecation, including fecal incontinence and urgency, should be carefully evaluated before considering POP surgery.
- Treatment of POP may ameliorate symptoms of sexual dysfunction. Still, dyspareunia has been associated with some types of POP repair, and, as such, changes in sexual function are an important aspect of preoperative counseling.
- Gynecologic and obstetric history, including gravity, parity, and hormonal status.
- Determination of whether the patient is premenopausal, perimenopausal, or post-menopausal and whether she has used any exogenous hormones such as oral contraceptives or local or systemic hormone replacement therapy
- Treatment expectations and an understanding of the balance between benefits and risks/burden of available treatment options.
- Whether the patient is aware of any prolapse and what, if any, symptomatology and bother the prolapse may be causing.
- Physical examination
- External genitalia: general appearance, estrogen status, lesions, and labial size, and adhesions.
- Estrogen status can be evaluated based on the presence or absence of a urethral caruncle, urethral prolapse, and/or labial adhesions, all of which, if present, may indicate estrogen deficiency.
- Attention to the overall tissue appearance and color is important. Hormonally deficient vaginal tissue has a pale, flat, dry appearance with no rugae, as opposed to the healthy, pink rugated tissue of well-estrogenized tissue
- Assessment of prolapse ideally should be performed in both the lithotomy and standing position
- Anal sphincter tone, which is a reflection of the function at S2-4, is particularly important in neurologic patients with pelvic floor dysfunction.
- External genitalia: general appearance, estrogen status, lesions, and labial size, and adhesions.
- History
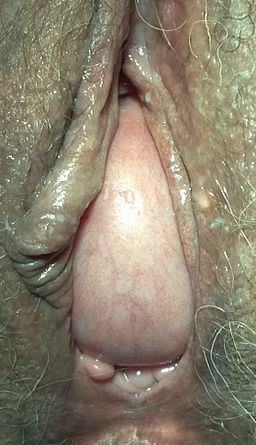
Stage 4 cystocele
Source: Wikipedia
- Imaging
- For most clinicians, radiologic studies play a relatively small role in the evaluation of POP
Pelvic Organ Prolapse Quantification (POP-Q) system
- Several classification systems are used to quantify pelvic organ prolapse, the most widely used of which are the Baden-Walker classification and the Pelvic Organ Prolapse-Quantification (POP-Q) system.
- POP-Q
- See Interactive Pop-Q Tool
- 6 defined points (Aa, Ba, C, D, Ap, Bp) and 3 other landmarks (GH, TVL, PB)
- Each is measured in centimeters in relationship to a fixed reference point, the hymenal ring
- A negative number represents above or proximal to the hymen
- A positive number represents below or distal to the hymen
- The hymen was selected as the reference point rather the introitus because it is more precisely identified
- Anterior wall (2):
- Aa
- Point denoting the anterior vaginal wall that is 3 cm proximal to the urethral meatus
- Meant to estimate the position of the bladder neck/proximal urethra junction in most women.
- Ranges from −3 cm to +3 cm (−3 cm in the absence of prolapse or urethral hypermobility).
- Ba
- Point denoting to the most distal portion of anterior vaginal wall prolapse (from the vaginal apex to point Aa).
- Ranges from −3 cm to +tvl
- Posterior wall (2)
- Ap
- Point denoting the posterior vaginal wall that is 3 cm proximal to the urethral meatus, meant to parallel the Aa point
- Ranges from −3 cm to +3 cm (−3 cm in the absence of prolapse or urethral hypermobility).
- Bp
- Point denoting to the most distal portion of posterior vaginal wall prolapse
- Ranges from −3 cm to +tvl
- Apex (2):
- C
- Point denoting the cervix (or the vaginal cuff/hysterectomy scar in women without a cervix)
- D
- Point denoting the posterior fornix (in a woman who still has a cervix)
- Point D, when compared to point C, will differentiate cervical elongation from uterine prolapse
- Genital hiatus (gh)
- Measured from the middle of the urethral meatus to the posterior midline hymen.
- Perineal body (pb)
- Measured from the posterior margin of the genital hiatus to the middle of anal opening.
- Total vaginal length (tvl)
- Greatest depth of the vagina in cm when the vagina is fully reduced (point C or D reduced to normal position).
- POP-Q staging
- Stages are assigned to the most severe portion of the prolapse when the full extent of the prolapse has been demonstrated with straining
- Points Aa, Ba, Ap, Bp, C, and D are measured with the patient straining, so as to accentuate maximal prolapse during the examination.
- Stage 0: without prolapse (points Aa, Ba, Ap, Bp are all at −3, and point C or D is between −tvl and −[tvl −2]) cm.
- Stage 1: distal portion (Ba or Bp) of the prolapse is > 1 cm above the level of the hymen
- Stage 2: distal portion (Ba or Bp) of the prolapse is within 1 cm on either side of the hymen
- Stage 3: distal portion (Ba or Bp) of the prolapse is > 1 cm below the hymen but not totally everted (no further than 2 cm less than tvl)
- Stage 4: complete vaginal eversion (≥ 2 cm less than tvl)
- Asymptomatic stage 1 or 2 POP are considered normal in adult women
Management
- Anterior wall prolapse
- Pessary
- Prolapse repair
- Apical prolapse
- Sacrocolpopexy
- Sacral pain and osteomyelitis have been described after suspensions of the uterus, cervix, or vagina to the sacrum
- CARE trial
- Population: women with prolapse without pre-opertative SUI
- Randomized to sacrocolpopexy +/- Burch colposuspension
- Results:
- Significantly higher incontinence rate at all points of follow-up in the women who did not undergo a Burch
- Posterior repair
- Levator ani, gluteal pain, and rectal penetration have been described after rectocele repairs performed with mesh augmentation
- In 2011, the FDA released a safety communication (FDA website) regarding mesh placed transvaginally specifically for the repair of pelvic prolapse.
- The communication specifically excluded slings and transabdominally placed mesh for prolapse repair
- The communication specifically excluded slings and transabdominally placed mesh for prolapse repair
Questions
- What organs are involved with anterior, apical, and posterior prolapse? Which is most common? Least common? Which level of support is lost with each prolapse?
- List risk factors for pelvic organ prolapse
- List causes of transient incontinence
- What do the Aa, Ba, Ap, Bp, C, and D points on the POP-Q system signify?
- Describe the stages of POP
Answers
- What organs are involved with anterior, apical, and posterior prolapse? Which is most common? Least common? Which level of support is lost with each prolapse?
- List risk factors for pelvic organ prolapse
- List causes of transient incontinence
- DIAPPERS
- Delirium
- Infection
- Atrophic vaginitis/urethritis
- Psychological
- Pharmacological
- Elevated urine output
- Reduced mobility
- Stool impaction
- What do the Aa, Ba, Ap, Bp, C, and D points on the POP-Q system signify?
- Describe the stages of POP
References
- Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Partin AW, Peters CA (eds): CAMPBELL-WALSH UROLOGY, ed 11. Philadelphia, Elsevier, 2015, chap 71
- Persu C, Chapple CR, Cauni V, Gutue S, Geavlete P. Pelvic Organ Prolapse Quantification System (POP-Q) - a new era in pelvic prolapse staging. J Med Life. 2011;4(1):75-81.