INFECTIONS & INFLAMMATION: SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS
Includes parts of CUAJ 2019 Penile Lesions Review
Epidemiology
- Most common bacterial STI in the US (descending order):
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhea
- Risk factors:
- Number of lifetime sex partners
- Unprotected sex without use of a condom
- Risky sex partners
- Effect of alcohol or drugs on sexual decision making
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Screening Recommendations
- Females
- Annual chlamydia screening for all sexually active women age ≤ 25, as well as for women with risk factors such as new or multiple sex partners.
- Annual gonorrhea screening for at-risk sexually active women, including women with new or multiple sex partners, or women who are living in areas with high rates of disease.
- Syphilis, HIV, and chlamydia screening for all pregnant women, and gonorrhea screening for at-risk pregnant women starting early in pregnancy, with repeat testing as needed.
- Males
- At least once-per-year screening for syphilis, chlamydia, gonorrhea, and HIV for all sexually active gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men (MSM).
- Men who have multiple or anonymous partners should be screened more frequently for STIs, at 3- to 6-month intervals. More frequent screening is also recommended for MSM who use illicit drugs, particularly methamphetamine, or whose sex partners use them.
- Reportable diseases in every US state (5):
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhea
- Syphilis
- Chancroid
- HIV/AIDS
Urethritis
- Urethritis, or urethral inflammation, can be the result of STIs.
- Classified as gonococcal vs. non-gonococcal
- Gonococcal Urethritis
- Caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, a gram-negative diplococcus
- An oxidase positive culture on Thayer-Martin medium is diagnostic of Neisseria gonorrhea
- Incubation period: 3-14 days
- Non-gonococcal urethritis (NGU)
- Caused by organisms other than Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Chlamydia trachomatis accounts for 15-40% of cases of NGU, with less common causes including Mycoplasma genitalium, Trichomonas vaginalis, adenoviruses, and herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1)
- Chlamydia
- Gram-negative
- Incubation period: 3-14 days (same as gonorrhea)
- Mycoplasma genitalium
- Mycoplasmas lack a cell wall and cannot be Gram stained.
- Can become intracellular, which can establish a chronic infection and aid in avoidance of both immune response and antibiotics
- Risk factors in men are young age, sexual intercourse in the past month, and a sex partner with a recent history of STI diagnosis or treatment
- Ureaplasma
- The evidence for Ureaplasma as a causative agent in NGU is conflicting
- Trichomonas vaginalis
- Flagellated parasite that exclusively infects the urinary tract
- Common vaginal pathogen but also can cause urethritis in men
- Caused by organisms other than Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Natural History
- Gonorrhea
- Complications in females: pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), tubal scarring, infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and chronic pelvic pain
- Can increase the risk of contracting and transmitting HIV
- Disseminated gonorrhea is rare today but can produce arthritis, dermatitis, meningitis, and endocarditis.
- Chlamydia
- The major health risk of untreated chlamydial infections in men is transmission to their female partners resulting in PID
- Complications in males include epididymitis and Reiter syndrome (conjunctivitis, urethritis, and reactive arthritis)
- Ascending chlamydial infection in females can result in scarring of the fallopian tubes, PID, risk for ectopic pregnancy, pelvic pain, and infertility
- Diagnosis and Evaluation
- History and Physical Exam
- History
- Symptoms of urethritis include urethral discharge, pruritus, and dysuria
- Gonorrhea
- Campbell’s: Men will usually have symptoms that cause them to seek treatment soon enough to prevent transmission to others. This could include urethritis, epididymitis, proctitis or prostatitis.
- CUAJ Penile Lesions Review 2019: In men, it is most often asymptomatic, but symptoms can include dysuria or mucopurulent discharge. [but multiple sources including Public Health Ontario and UptoDate say gonorrhea is symptomatic in most men)
- Women are frequently asymptomatic.
- Campbell’s: Men will usually have symptoms that cause them to seek treatment soon enough to prevent transmission to others. This could include urethritis, epididymitis, proctitis or prostatitis.
- Chlamydia
- Symptoms in males include dysuria, urethral discharge, and epididymitis
- [UptoDate] up to 42% of men with NGU are asymptomatic
- Up to 75% of women with chlamydial infection can be asymptomatic.
- Symptoms in males include dysuria, urethral discharge, and epididymitis
- Mycoplasma genitalium
- Most infected patients are symptomatic, but ≈25% may have asymptomatic urethral infection
- Labs
- Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) performed on urine
- Can be used to look for gonorrhoeae and chlamydia
- All patients should be tested for both gonorrhea and chlamydia, given the high association of co-infection.
- Culture and hybridization tests that require urethral swab specimens are available. However, NAATs are preferred because of their higher sensitivity, and urethral swabs are no longer recommended for evaluation of urethritis
- Culture for Mycoplasma genitalium is very difficult, and the diagnosis is made by NAATs or polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
- NAAT has replaced wet mounts and culture for diagnosis of trichomonas vaginalis
- Can be used to look for gonorrhoeae and chlamydia
- Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) performed on urine
- History
- Management
- Antibiotics
- Current treatment of uncomplicated gonococcal infections involves ceftriaxone 250 mg IM single dose with
- Azithromycin 1 gm PO x single dose or
- Doxycycline 100 mg PO BID x 7 days
- Dual therapy is required for both N. gonorrhoeae and chlamydia because of the high rate of coinfection
- Current treatment of uncomplicated gonococcal infections involves ceftriaxone 250 mg IM single dose with
- All persons with gonorrhea should be tested for other STIs including syphilis and HIV
Ulcerative lesions of the male genitals
- Classified as infectious vs. non-infectious
| Infectious (5) | Non-infectious (6) |
|
|
- Infectious
- Epidemiology
- In sexually active young US men, genital herpes is most common type of ulcer followed by syphilis
- Chancroid occurs in some parts of the US
- Lymphogranuloma venereum is increasing in incidence in MSM, including in the US.
- Donovanosis/granuloma inguinale is endemic in some tropical and developing areas, including India; Papua, New Guinea; the Caribbean; central Australia; and southern Africa but usually does not occur in the US
- Diagnosis and Evaluation:
- History and physical exam
- Labs:
- Herpes: Culture or NAAT/PCR testing for HSV, and diagnostic serology for determining the specific type of HSV
- Syphilis: serologic testing and a darkfield examination if possible
- Chancroid: testing for H. ducreyi should be performed in environments where chancroid is prevalent
- Patients who are not known to be HIV positive should be tested for HIV
- Even after complete diagnostic evaluation, 25% of patients with genital ulcers will have no laboratory-confirmed diagnosis.
- Biopsy of ulcers is indicated if they are unusual or do not respond to initial therapy
- Epidemiology
- Herpes
- Most common cause of genital ulcers
- Caused by the herpes simplex virus, a double-stranded DNA virus
- HSV-1 causes mainly oral infections but now accounts also for 5-30% of first episodes of genital HSV infections
- HSV-2 causes the majority of genital herpes and is transmitted by sexual contact
- Females are more susceptible to HSV-2 infection and are more likely to have symptomatic infections. Most HSV-2 transmission thus occurs from individuals who do not know they are infected
- HSV-2 infection seems to protect against HSV-1 infection, but HSV-1 gives only a small amount of protection from infection with HSV-2
- Pathophysiology
- HSV initiates replication in epithelial cells at the site of entry, damages the cells, and enters the ends of peripheral sensory nerves. Once in the nerve cell body, HSV enters a latent state
- Recurrence and reactivation of virus occur with transportation in the peripheral nerves back to the mucosal or skin surface.
- Events that trigger reactivation of HSV include local trauma such as surgery or ultraviolet light, immunosuppression, or fever
- Incubation period: 4-7 days after sexual intercourse
- Diagnosis and Evaluation
- History and Physical Exam
- History
- Patients have pain, burning, or itching, and 80% of women report dysuria.
- Other associated symptoms include flu-like symptoms, fever, headache, malaise, and myalgias.
- Possible complications include aseptic meningitis and autonomic dysfunction that can lead to urinary retention
- Physical Exam
- The classic first presentation of primary herpes is clusters of erythematous papules and vesicles on the external genitalia that do NOT follow a neural distribution
- Tender inguinal and femoral lymph nodes may be present.
- Over the next 2- 3 weeks, 75% of patients have new lesions, which can progress to vesicles and pustules and can coalesce into ulcers before crusting and healing
- Primary genital HSV-1 infection cannot be distinguished from HSV-2 infection on clinical examination alone, but requires laboratory testing.
- History
- History and Physical Exam
Genital Herpes
Souce: Wikipedia
- Labs
- Options: NAAT or cell culture of a lesion
- NAAT is preferred due to increased sensitivity, and viral cultures are limited by the rate of viral shedding that can be intermittent and, therefore, cause false-negative results
- While the Tzanck preparation has historically been used, it should not be solely relied upon as it is non-specific and insensitive.
- In patients with no active lesions, serology must be used; specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) testing can distinguish the two types of HSV
- Options: NAAT or cell culture of a lesion
- Recurrent episodes
- Genital HSV-1 recurs much less frequently than genital HSV-2 infections
- HSV recurrences decrease after the first year
- Management
- Treatment for a first clinical episode should be started on clinical grounds before laboratory confirmation of diagnosis.
- Currently available medications do not eradicate the virus, but aim to reduce the signs and symptoms of infection and prevent new lesions.
- Treatment of recurrent episodes reduces their severity and duration.
- Oral therapy within 24 hours of the first signs or symptoms of recurrence increases the chance of resolving a recurrence without lesions
- Treatment of recurrent episodes reduces their severity and duration.
- Options (3): -clovir
- Acyclovir (intravenous only)
- May be needed for those with neurologic complications, those unable to take oral medications, or those with widespread disease (e.g., immunocompromised patients)
- Valacyclovir
- Famciclovir
- Acyclovir (intravenous only)
- Treatment is usually 7 to 10 days but should be extended if lesions are not adequately healed
- Lesions heal in 5-10 days in the absence of antiviral treatment
- Syphilis
- Caused by Treponema pallidum
- Primary syphilis
- Incubation period: typically 2-3 weeks, can range from 9-90 days for the appearance of lesions after infection
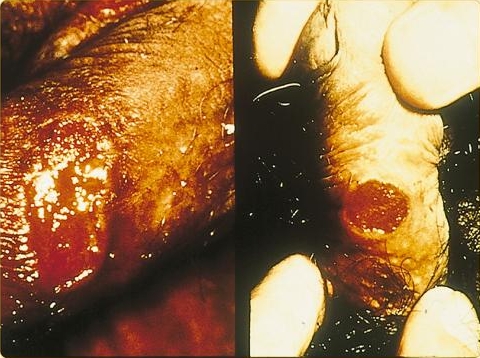
- Lesion
- Called “chancre”
- Occurs at the initial site of infection
- In male, lesions are typically on the glans, corona or perineal area
- In females, lesions are typically on the labia or perianal area
- Usually single and painless but can be multiple, and up to 25% of chancres can be painful
- See Figure
- Local non-tender lymphadenopathy is common
- Untreated lesions heal spontaneously in 3-8 weeks
- Secondary syphilis
- T. pallidum eventually becomes a systemic infection with bacteremia.
- Appears 3-5 months after the initial infection
- Characterized by a maculopapular rash, which is often widespread and involves the scalp, palms, and soles of the feet.
- The rash can ulcerate and lead to condyloma lata, which are wart-like lesions.
- Additional symptoms include fever, malaise, weight loss, patchy alopecia, and ocular inflammation
- A broad vasculitis occurs in ≈10% of patients and may lead to hepatitis, iritis, nephritis, and neurologic problems including headache and cranial nerve involvement, especially VIII (auditory).
- Relapses usually occur in the first year after infection and rarely after the second year. The infection then becomes latent and asymptomatic.
- Latent syphilis is defined as seroreactivity with no clinical evidence of disease
- Tertiary or late syphilis
- ≈35% of individuals with late latent syphilis will develop the late manifestations of syphilis, which include neurosyphilis, cardiovascular syphilis, and gummatous syphilis.
- Diagnosis and Evaluation
- Labs
- Darkfield examination
- Cultures of T. pallidum are not possible
- Direct tests include identification of T. pallidum under a dark-ground microscope
- Serology
- Categories of tests (2):
- Non-treponemal (directed against phospholipids)
- Treponemal (directed against T. pallidum polypeptides)
- Non-treponemal
- Includes:
- Rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test
- Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) test
- Toluidine red unheated serum test (TRUST)
- Need confirmation with a treponemal test because they can be positive in other conditions such as:
- Viral infections
- Pregnancy
- Malignancies
- Autoimmune disease
- Advanced age
- Used to monitor disease activity
- Includes:
- Treponemal tests
- Includes
- FTA-ABS: fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test
- MHA-TP: microhemagglutination assay for T. pallidum
- TP-HA: T. pallidum hemagglutination assay
- TP-PA: T. pallidum particle agglutination test
- Includes
- Categories of tests (2):
- All patients with syphilis should be tested for HIV
- Darkfield examination
- Labs
- Management
- Antibiotics
- Standard treatment for all stages of syphilis is benzathine penicillin G
- Stage and clinical manifestations of syphilis determine the preparation, dosage, and length of treatment
- Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction
- Not an allergic reaction to penicillin but occurs with treatment of the treponemes, and more commonly with treatment with penicillin and in early syphilis.
- Consists of fever, malaise, nausea, and vomiting; may also be associated with chills and exacerbation of secondary rash.
- Management
- Bed rest and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications.
- Standard treatment for all stages of syphilis is benzathine penicillin G
- Antibiotics
- Chancroid
- Caused by H. ducreyi (gram-negative coccobacilli)
- Initial presentation of a papule that may progress to anogenital painful ulceration and lymphadenitis with progression to bubo formation
- Incubation period: 3-10 days
- Most common site of infection: prepuce
- Diagnosis and Evaluation
- Labs
- Definitive diagnosis requires culture on media not routinely available.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggests that a probable diagnosis of chancroid can be made if:
- The patient has one or more painful ulcers
- No evidence of T. pallidum is present on darkfield examination of ulcers or by serologic testing for syphilis performed at least 7 days after onset of the ulcers
- Ulcers and lymphadenopathy, if present, are typical for chancroid
- Results of tests for HSV on the ulcer exudate are negative
- Chancroid, like genital herpes and syphilis, is a risk factor for transmission of HIV; patients should be tested for HIV at the time of diagnosis of chancroid
- Labs
- Management
- Options:
- Azithromycin 1g in a single dose or
- Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM in single dose or
- Ciprofloxacin 500 mg orally BID x 3 days or
- Erythromycin base 500 mg orally TID x 7 days
- Options:
- Lymphogranuloma venereum
- Caused by chlamydia
- A self-limited genital ulcer or papule is sometimes present at the site of infection but usually has disappeared by the time of presentation. The secondary stage is the most common presentation in heterosexuals and is marked by tender inguinal and/or femoral lymphadenopathy, typically unilateral
- Inguinal lymphadenopathy are more common in males because the lymph drainage of the cervix and vagina are to the retroperitoneal rather than the inguinal lymph nodes
- Lymphogranuloma venereum proctocolitis can mimic inflammatory bowel disease, and complications include chronic colorectal fistulas and strictures
- Diagnosis and Evaluation
- Labs
- Swab of lesions or aspiration of buboes from genitals or lymph node, sent for culture, direct immunofluorescence, or nucleic acid detection
- Labs
- Management
- Doxycycline 100 mg orally BID x 21 days
- Donovanosis/Granuloma inguinale
- Caused Klebsiella granulomatis (intracellular gram-negative bacterium)
- Does not usually occur in the US
- The disease manifests as painless, slowly progressive ulcers on the genitals and perineum. Despite the name, inguinal involvement is uncommon (10%), but tender if present
- Lesions
- Described as beefy red because of high vascularity, and they bleed easily
Beefy red lesion characteristics of donovanosis/granuloma inguinale.
Source: Wikipedia
- Diagnosis and Evaluation
- Labs
- Requires visualization of dark-staining Donovan bodies on crush preparation or biopsy
- Labs
- Management
- Doxycycline 100 mg PI BID for at least 3 weeks and until all lesions have healed
UrologySchool.com Summary of Sexually Transmitted Infections
Disease |
Infectious agent |
Lesions |
Lymphadenopathy |
Systemic symptoms |
Testing |
Treatment |
Genital herpes |
HSV-1, HSV-2 |
PAINFUL vesicles, shallow, usually multiple |
Tender, bilateral inguinal lymphadenopathy |
Present during primary |
NAAT or cell culture, serology for HSV subtype |
-cyclovir |
Primary syphilis/chancre |
Treponema pallidum |
PAINLESS, indurated, with a clean base, usually singular |
Non-tender, rubbery, nonsuppurative bilateral lymphadenopathy |
None |
Dark field examination, serology |
Benzathine penicillin G |
Chancroid |
H. ducreyi |
Painful papule, then undermined purulent ulcer, single or multiple |
Tender, regional, painful, suppurative lymphadenopathy |
None |
Culture on media not routinely available |
Azithromycin |
Lymphogranuloma venereum |
Chlamydia |
Small, PAINLESS, singular, vesicle or papule progresses to an ulcer |
Tender, matted, large lymphadenopathy with fistulous tracts |
Present after genital lesion heals |
|
Doxycycline |
Donovanosis/Granuloma inguinale |
Klebsiella |
PAINLESS, multiple slowly progressive ulcers on the genitals and perineum |
Not present |
|
Donovan bodies |
Doxycycline |
Other genital lesions
- Human papillomavirus (HPV)
- Pathogen
- Double-stranded DNA virus
(similar to herpes)
- Non-oncogenic subtypes: 6 and 11; account for ≈90% of anogenital warts, also known as condyloma acuminata
- Oncogenic subtypes: 16 and 18; account for cervical cancer and other types of anogenital cancer including penile, vulvar, vaginal, anal cancers; subtype 16 more important for penile cancer
- Double-stranded DNA virus
(similar to herpes)
- Epidemiology
- > 50% of sexually active persons will become infected at least once in their lifetime
- Natual history
- ≈70% of HPV infections resolve spontaneously in 1 year and 90% in 2 years, and HPV persistence develops in the remaining persons
- Pathogenesis
- Transmission can occur from asymptomatic and subclinical patients.
- Among asymptomatic females in the general population, the prevalence of HPV infection ranges from 2-44%, and among men from 2-35%
- Risk factors: presence of foreskin, increasing numbers of sexual partners, lack of condom use, and smoking.
- Transmission can occur from asymptomatic and subclinical patients.
- Diagnosis and Evaluation
- See Figure
- HPV warts can also occur in the urethra and can cause hematuria, dysuria, or difficulty voiding
- Management
- The goal of treatment is removal of the warts; treatment will not eradicate the infection.
- Treatment is guided by wart size, number, and location, and patient preference.
- Options classified as patient-applied vs. provider-administered modalities
- Patient-applied (3):
- Imiquimod cream
- Podofilox cream
- Sinecatechins ointment
- Provider-administered (4):
- Podophyllin (less refined form of podofilox)
- Trichloroacetic acid
- Cryotherapy
- Surgical therapy including direct excision with scissors, tangential shave excision, curettage, or laser therapy using a CO2 laser
- See Table 1 from 2019 CUAJ Penile Lesions Review
- HPV vaccine
- Designed to prevent infection and are not effective in clearing an infection once established
- Recommended for females AND males age < 26, preferably to start before onset of sexual activity.
- Gardasil
- Quadrivalent HPV vaccine that provides protection against HPV types 6, 11, 16, and 18.
- Cervarix
- Bivalent HPV vaccine that provides protection against HPV types 16 and 18
- Scabies
- Skin infection caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei
- Pathogenesis
- The female lays eggs in the skin, and transmission is by person-to-person skin-to-skin contact with passage of pregnant female mites.
- Incubation period: 2-6 weeks
- Diagnosis and Evaluation
- History and Physical Exam
- Most common symptoms are skin rash and itching, especially at night, from an allergic reaction to the mite proteins.
- Other
- Microscopic examination of a skin scraping to assess for mites, mite eggs, or fecal matter (scybala)
- History and Physical Exam
- Management
- Permethrin cream or ivermectin 200 μg/kg orally
- Pediculosis Pubis (Phthirus pubis): Pubic or Crab Louse
- Lice are obligate bloodsucking parasites of humans
- Transmission requires close contact
- The typical presentation is pruritus, which is caused by a delayed hypersensitivity reaction to the lice, and is usually worse at night and after baths
Pubic lice in genital area
Source: Wikipedia
- Management
- Permethrin 5% cream rinse applied to affected areas and washed off after 10 minutes or pyrethrins with piperonyl butoxide applied to affected areas and washed off after 10 minutes
- Molluscum Contagiosum
- A superficial skin disease caused by the pox virus
- Can be sexually transmitted
- Characteristic lesions are small, discrete waxy papules 3-5 mm in diameter, with a central depression
- Diagnosis is generally on the basis of the characteristic appearance of skin lesions.
- The infection is usually self-limited and spontaneously disappears in 6-12 months, but may take up to 4 years to resolve. However, infection in immunocompromised individuals, such as those with HIV, is typically more severe and extensive.
- Candidal infections
- The most common clinical syndromes caused by Candida albicans include genital mild burning and pruritus with erythema of the glans and/or the prepuce, and subpreputial discharge.
- Risk factors for fungal balanitis (especially Candida balanitis):
- Diabetes mellitus
- HIV infection
- Iatrogenic immunosuppression
- Presence of foreskin
- Widespread use of antibiotics
- Management
- The guidelines for the treatment of Candida balanitis have not yet been standardized.
- Treatment options usually involve topical antifungal therapy, either associated or not with systemic antifungal treatment.
- Azole agents, such as clotrimazole, miconazole, econazole, fluconazole, and itraconazole, are the usually recommended antifungal agents
Vaginitis
- Vaginal infections are characterized by discharge, itching, or odor.
- Bacterial vaginosis is the most common diagnosis in females seeking care for vaginal symptoms
- Diseases most frequently associated with vaginal discharge (3):
- Bacterial vaginosis (BV)
- Trichomoniasis
- Candidiasis
- Bacterial vaginosis I have no CLUE why there are FISH in my GARDEN
- Pathogenesis
- Caused by replacement of the normal hydrogen peroxide–producing Lactobacillus species in the vagina with high concentrations of anaerobic bacteria including Prevotella, Mobiluncus, GARDNErella vaginalis, Ureaplasma, Mycoplasma, and other fastidious anaerobes.
- Not sexually transmitted§, partner does not need to be treated
- Diagnosis and Evaluation
- Although BV is the most common diagnosis in females seeking care for vaginal symptoms, most females with BV are asymptomatic
- Characteristic findings for BV on microscopic examination are CLUE cells; discharge can have FISHY odour
- Management: metronidazole; partner does not require treatment
- Trichomoniasis
- Pathogenesis
- Caused by the protozoan T. vaginalis
- Sexually transmitted
- Diagnosis and Evaluation
- The discharge is diffuse, malodorous, and yellow green with vulvar irritation
- A strawberry rash on the vulva or strawberry cervix may be seen
- Diagnosis is usually by microscopy of vaginal secretions showing the Trichomonas organisms
- Management: metronidazole; partner needs to be treated
- Candidiasis
- Pathogenesis
- Usually caused by Candida albicans but occasionally by other species of Candida or yeasts
- Diagnosis and Evaluation
- The diagnosis is made via wet prep with saline or KOH, a Gram stain of vaginal discharge that demonstrates yeast, hyphae, or pseudohyphae, or a culture that shows Candida or other yeast species.
- Wet mounts should first be done for all patients, and culture used for those with symptoms with negative wet mounts.
- The diagnosis is made via wet prep with saline or KOH, a Gram stain of vaginal discharge that demonstrates yeast, hyphae, or pseudohyphae, or a culture that shows Candida or other yeast species.
- Management
- Uncomplicated vulvovaginal candidiasis: over-the-counter intravaginal agents including butoconazole or clotrimazole creams, miconazole as a cream or intravaginal suppository, or tioconazole ointment.
Epididymitis
- See Inflammatory and Painful GU Conditions Chapter Notes
HIV/AIDS
- HIV is a single stranded RNA retrovirus that infects CD4 helper T cells and dendritic cells
- The HIV envelope precursor protein gp160 is cleaved into gp 120 and gp41
- Factors associated with increased risk of seroconversion with HIV after a needle stick (4):
- Deep as opposed to superficial exposure
- Visible blood on the injuring device
- Prior placement of the injuring device in an artery or vein
- Patient dying within 2 months of the exposure
- Diagnosis and Evaluation
- The initial test is a screening test for antibodies, the conventional or rapid enzyme immunoassay (EIA). The initial result can be obtained in 30 minutes.
- Positive or reactive screening tests must be confirmed by a supplemental antibody test, Western blot and indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA), or virologic test, the HIV-1 RNA assay. A positive confirmation test result establishes the diagnosis
- HIV is detectable in 95% of patients within 3 months after infection. During this initial 3-month period, the “window” period, the screening test result may be negative but the person may still be infected. Viral load assay is the best diagnostic test to detect HIV in the acute phase of infection
- The diagnosis of AIDS is made if the CD4 count is < 200 cells/mm3 or if there is a serious opportunistic infection, neoplasm, or other life-threatening condition.
- Urologic manifestation of HIV
- Infections
- Interaction with other STIs
- Testing for HIV is recommended in anyone with a diagnosed STI or who is at risk for an STI
- Genital ulcers bleed frequently during intercourse, potentially leading to increased infectiousness.
- Kidney infections
- Persons with HIV infection are more likely to develop clinical TB if infected, including renal and other extrapulmonary disease
- Mycobacterial infection of the kidney is detected at autopsy in 6-23% of AIDS patients
- Other kidney infections that occur in AIDS include CMV, aspergillus and toxoplasma
- Persons with HIV infection are more likely to develop clinical TB if infected, including renal and other extrapulmonary disease
- Prostatitis
- Prostate infection may be more common in men with HIV
- Prostatitis is usually caused by E. coli, but in HIV-infected males, many other organisms can cause prostate infection, including S. aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Serratia marcescens, Salmonella Typhi, Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium intracellulare, and CMV. Fungal infections also can cause prostatitis, particularly in immunocompromised patients with T-cell counts < 200 cells/μL.
- In men with HIV, cultures should be performed not only for the usual bacteria, but also for more atypical organisms including aerobes, anaerobes, fungi, and M. tuberculosis
- UTI
- Incidence of bacteruria is related to CD4 counts and viral load
- Unusual organisms may cause UTIs, including CMV
- Interaction with other STIs
- Testis, epididymis, and SVs
- HIV in semen is the main vector for transmission and can persist despite high loads of ART
- The most common intrascrotal pathology in men with HIV/AIDS is testicular atrophy. This can arise from endocrine imbalances, febrile episodes, malnutrition, testicular infections, and toxic effects of therapy
- HIV itself is thought to be cytotoxic to germ and Sertoli cells
- The testes may also be directly infected by opportunistic infections
- In combination with extra-testicular causes, testosterone levels fall with progressive HIV disease
- Erectile dysfunction
- Prevalence higher in HIV-infected men than uninfected
- HIV patients taking ART should be started on the lowest dose possible of PDE5 inhibitors
- PDE5 inhibitors depend on CYP3A for clearance, and all protease inhibitors and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors are inhibitors of CYP3A to some extent. This can lead to a significant increase in the serum dose of PDE5 inhibitors
- See 2018 AUA Erectile Dysfunction Guideline Notes for dosing adjustments required with use of PDE5i
- PDE5 inhibitors depend on CYP3A for clearance, and all protease inhibitors and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors are inhibitors of CYP3A to some extent. This can lead to a significant increase in the serum dose of PDE5 inhibitors
- Renal function
- The classic clinical presentation of HIV-associated nephropathy is rapidly progressive azotemia with severe proteinuria, often nephrotic range, and little or no peripheral edema
- Polymorphism of Apolipoprotein-1 is associated with development of HIV-associated nephropathy (HIVAN) in African-American patients
- Voiding dysfunction
- Increased incidence of LUTS
- Hematuria
- Higher rate of microscopic hematuria but HIV patients should be evaluated similarly to other individuals
- Stones
- One of the complications of some medications for treatment of HIV is stone formation. The protease inhibitors specifically may cause stone formation.
- Indinavir can form crystals in the urine. Indinavir stones are typically radiolucent on both plain film and CT scan but can also be mixed with calcium and appear radiopaque
- Newer inhibitors including lopinavir, atazanavir, amprenavir, and nelfinavir have also been associated with the development of stones, but with less frequency than reported for indinavir
- In patients with protease stones and in whom conservative management is possible as a first-line step, discontinuation of the drug and hydration should be tried
- Another type of stone reported to be more common in HIV patients is ammonium acid urate stones, possibly reflecting chronic diarrhea and malnutrition of chronic disease
- Neoplasms
- Infections
- Compared with the general population, patients with HIV have a greater risk to develop not only non–AIDS-defining cancers with a viral pathogenesis but also non–virus-related cancers
- AIDS-defining cancers (3):
- Kaposi sarcoma (KS)
- Most relevant for the urologist given the possibility of KS lesions on the penis
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Invasive cervical cancer in females
- Kaposi sarcoma
- See Penile Tumors Chapter Notes
- Human herpes virus 8 (KSHV/HHV-8), a double-stranded DNA virus is the causative pathogen in > 90% of cases
- Typically manifests with disseminated pigmented skin lesions, a few millimeters to several centimeters, from pink to purple or brown, often associated with edema and lymph node and visceral involvement in up to 50% of patients
- See Figure
- Non–AIDS-Defining Urologic Malignancies
- HIV is associated with an increased risk of
- Testicular tumours
- HIV-infected men are also at risk for testicular non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Kidney cancer
- Penile cancer
- Note that the 2018 EAU Guidelines on Penile Cancer state that “penile cancer is not linked to HIV or AIDS”
- HIV is not associated with increased risk of
- Prostate cancer
- Bladder cancer
- Use caution in deciding to use intravesical BCG in the treatment of HIV-positive patients. The effectiveness of BCG is dependent on a functioning immune system, and therefore the agent is not typically used in immunocompromised patient
Questions
- List the ulcerative genital lesions and the associated pathogen.
- Which ulcerative genital lesions present with tender lesion(s)?
- Which ulcerative genital lesions present with lymphadenopathy?
- Which subtypes of HPV are responsible for penile warts?
- What are the treatment options for penile HPV?
- What is the pathogen responsible for Kaposi Sarcoma?
- Which urologic malignancies are associated with HIV?
Answers
- List the ulcerative genital lesions and the associated pathogen.
- Herpes - HSV
- Syphillis - treponema pallidum
- Chancroid - H. Ducreyi
- Lymphogranuloma venereum - Chlamydia
- Donovanosis/granuloma inguinale - Klebsiella
- Which ulcerative genital lesions present with tender lesion(s)?
- Herpes
- Chancroid
- Which ulcerative genital lesions present with lymphadenopathy?
- Herpes: tender lymphadenopathy
- Syphillis: non-tender lymphadenopathy
- Chancroid: tender lymphadenopathy
- Lymphogranuloma venereum: tender lymphadenopathy
- Which subtypes of HPV are responsible for penile warts?
- 16
- 18
- What are the treatment options for penile HPV?
- Patient-applied (3):
- Imiquimod cream
- Podofilox cream
- Sinecatechins ointment
- Provider-administered (4):
- Podophyllin
- Trichloroacetic acid
- Cryotherapy
- Surgical therapy including direct excision with scissors, tangential shave excision, curettage, or laser therapy using a CO2 laser
- Patient-applied (3):
- What is the pathogen responsible for Kaposi Sarcoma?
- Human Herpes Virus 8
- Which urologic malignancies are associated with HIV?
- Testicular cancer
- Kidney cancer
- Penile cancer
References
- Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Partin AW, Peters CA (eds): CAMPBELL-WALSH UROLOGY, ed 11. Philadelphia, Elsevier, 2015, vol 1, chap 15