PEDIATRICS: ECTOPIC URETER, URETEROCELE, AND URETERAL ANOMALIES
Embryology
- Dysplasia is the product of inadequate ureteric bud-to-blastema interaction
Duplex kidney
- Definition of duplex kidney: a kidney with two ureters/collecting systems
- Most common congenital renal anomaly
- Pathogenesis
- Due to 2 separate ureteral buds on one side that induce upper and lower renal moieties.
- The ureteral bud is derived from the Wolffian duct
- If a single bud divides close to its origin, the result is an incomplete duplex kidney with a common distal ureter
- If two separate buds form, the kidney is drained by two separate ureters i.e. duplex kidney
- Due to 2 separate ureteral buds on one side that induce upper and lower renal moieties.
- May be completely normal, although it tends to be longer than normal, but if there is abnormal development:
- Ectopic ureteral insertion with or without a ureterocele is nearly always associated with the upper pole owing to its budding from the mesonephric duct later (more cephalad) than the lower pole ureteral bud
- Reflux and UPJO occur most often in the lower pole
- Factors contributing to vesicoureteral reflux:
- Lateral ureteral insertion
- Poorly developed trigone
- Gaping ureteral orifice
- Short intramural tunnel
- Lax bladder neck does not contribute to vesicoureteral reflux
- Factors contributing to vesicoureteral reflux:
- Weigert-Meyer rule: the ureteric orifice of the upper pole is inferior and medial to the lower pole ureteral orifice
- See Figure for visual representation of Weiger-Meyer
Ectopic Ureter
- Definition of ectopic ureter: any ureter, single or duplex, that does not enter the trigonal area of the bladder
- Females
- The ectopic ureter may enter anywhere from the bladder neck to the perineum and into the vagina and even rectum
- Because the ureteral bud derives from the wolffian duct, in females the ectopic ureter will not insert directly into the müllerian structures (vagina, cervix, uterus), but may be associated with the remnant of the wolffian duct, the Gartner duct, that runs alongside the mature müllerian structures
- A ruptured ureter may drain into the adjoining fallopian tube, uterus, upper vagina, or the urethra
- Never drains to ovary
- Continuous wetting is a classic symptom
- The ectopic ureter may enter anywhere from the bladder neck to the perineum and into the vagina and even rectum
- Males
- The ectopic ureter always enters above the external sphincter or pelvic floor
- Most common site of insertion: posterior urethra
- Can also enter into the wolffian structures, including vas deferens, seminal vesicles, or ejaculatory duct
- Clinical presentation is not incontinence but infection
- The ectopic ureter always enters above the external sphincter or pelvic floor
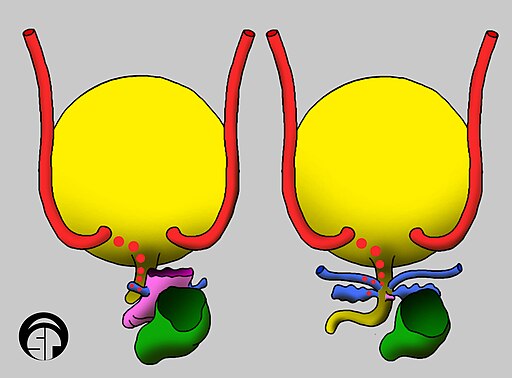
These two illustrations are posterior views of all the possible locations of ectopic ureter insertion (red dots) in a female (left illustration) and a male (right illustration). The different colors indicate embryologic origin of structure: a) red = metanephric duct (ureter), b) yellow = urogenital sinus (bladder and urethra), c) blue = Wolffian duct (Gartner's ducts in female, seminal vesicles and vasa deferentia in male), pink = Müllerian ducts (vagina in female, prostatic utricle in male), green = hindgut (rectum).
Source: Wikipedia
Ureterocele
- Definition of ureteroceles: a cystic dilation of the distal aspect of the ureter
- Epidemiology
- Occur most frequently in females (4:1 ratio) and almost exclusively in whites
- Pathogenesis
- Classic explanation of ureterocele formation: distal ureteral expansion is produced by failure of rupture of a distal membrane at the ureteral orifice (Chwalle membrane)
- ≈10% are bilateral
- 80% arise from the upper poles of duplicated systems, and ≈50% will have associated vesicoureteral reflux
- Classified into intravesical (located with the bladder) vs. extravesical (spanning the bladder neck and urethra)
Clinical Presentation
- Both ureterocele and ectopic ureter
- Imaging
- The majority of ureteroceles and ectopic ureters are detected through prenatal ultrasound imaging, even if the specific diagnosis is not made until after birth
- With a tentative diagnosis of a ureterocele or ectopic ureter, careful evaluation of the other renal units and bladder should be made
- The most obvious imaging sign on ultrasonography of an ectopic ureter is a tortuous dilated ureter due to distal obstruction.
- This is not always present, but when seen should direct further attention to the distal ureter and bladder to also assess for the presence of a ureterocele, which would appear as a cystic structure in the bladder.
- The upper pole may be dysplastic, but cystic changes are uncommon.
- The lower pole is usually normal, but may be hydronephrotic, yet uncommonly echogenic. The lower pole is displaced laterally, not medially.
- The report of an upper pole “cyst” in a fetus should be interpreted as being upper pole hydronephrosis until proven otherwise
- Infection
- Remains a significant reason for clinical presentation of both ectopic ureters and ureteroceles, which may occur at any age and have a highly variable pattern
- Ectopic ureters will frequently manifest with a less acute pattern than ureterocele, evidenced by ongoing low-grade fever with periodic spikes.
- In some cases, urine cultures will be negative because the infected ectopic system is not draining into the bladder
- Boys may present with a subacute pattern of infection, but more often these boys have epididymitis; in the setting of a suspicion for epididymitis in a young boy, an ultrasound is performed of the upper tracts to ensure no abnormality
- Ectopic ureter specific
- Incontinence
- Due to site of insertion (see above), incontinence may be present in a girl, but not in a boy
- The toilet-trained girl with continuous urinary leakage must be evaluated for an ectopic ureter. Imaging may not immediately detect this condition because the affected renal moiety may not be dilated
- Ureterocele specific
- Prolapse
- Ureterocele prolapse is usually a smooth, congested mucosal-covered intralabial mass, and the child may have difficulty voiding
- The mass
- Protrudes from the urethra (distinct from the vagina)
- Not circumferential (distinct from urethral prolapse)
- Not lobulated (distinct from sarcoma botryoides)
- Colour may vary from pink to bright red to the necrotic shades of blue, purple, or brown
- See Figure
- Bladder outlet obstruction secondary to ureterocele is possible but uncommon
- The ureterocele usually slides down the posterior wall of the urethra and, hence, the urethra can be demonstrated anterior to the mass and can be catheterized.
- Puncture of the prolapsed ureterocle is the most appropriate initial management
- The prolapsing ureterocele may be manually reduced back into the bladder; however, even if this is successful, the prolapse is likely to recur.
Diagnosis and Evaluation: H+P, US (bladder views), VCUG, DMSA, cystoscopy
- History and Physical exam
- Imaging
- Ultrasound
- Will usually provide the anatomic diagnosis of an ectopic ureter or ureterocele and allow an inference of renal function
- Typical findings are dilated upper pole with ureteral dilation or a dilated single system.
- Above the bladder: cannot differentiate between a dilated ectopic ureter and ureterocele
- Bladder images are critical to distinguish them because management is very different
- Bladder views: differentiates ureterocele from ectopic ureter
- Ureterocele is characterized by a thin-walled, cystic dilation within the bladder and not extending beyond its walls [ectopic ureter may have dilation beyond the bladder walls?]
- A very dilated ectopic ureter may produce an impression on the bladder and appear as a ureterocele
- Magnetic Resonance Urography
- Occasionally, the renal parenchyma associated with an ectopic ureter is difficult to locate on ultrasound and may be identified only by alternative imaging studies. In such cases in which an ectopic ureter is strongly suspected because of incontinence yet no definite evidence of the upper pole renal segment is found, CT or MRI has demonstrated the small, poorly functioning upper pole segment.
- Functional Assessment
- Bladder Function: VCUG
- Most definitive evaluation of the bladder and distal ureters, as well as the urethra
- An obligatory imaging test and should almost always be obtained before any intervention to define the baseline situation
- Excretory urography often demonstrates the characteristic cobra head (or spring-onion) deformity: an area of increased density similar to the head of a cobra with a halo or less dense shadow around it. The halo represents a filling defect, which is the ureterocele wall, and the oval density is contrast material excreted into the ureterocele from the functioning kidney.
- The appearance of the bladder base with filling and voiding will be useful in therapeutic decisions, as massive eversion indicates a weak trigonal floor that may be more likely to require surgical repair
- Can usually demonstrate the size and laterality of the ureterocele as well as the presence or absence of vesicoureteral reflux.
- If early filling views are not obtained, the ureterocele may efface and the filling defect may not be visible.
- In some cases the ureterocele will evert and appear as a diverticulum.
- Renal Function: Radionuclide nuclear imaging
- Gold standard for renal functional assessment; usually best provided by DMSA imaging
- The function of the affected upper pole is the principal focus, but the health of the other renal moieties must be determined as well, particularly if there is lower pole reflux or hydronephrosis of any unit.
- Cystoscopy
- Should take note of the character of the urethra, bladder neck, and trigone relative to the ureterocele or ectopic ureter
Management
- The goals of therapy are:
- Preservation of renal function (primary concern for both ectopic ureter and ureterocele)
- There are few objective criteria to indicate how much residual function is worth preserving.
- Elimination of infection, obstruction, and reflux
- Primary vesicoureteral reflux develops due to the combined effects of the lateral ureteral orifice position, the ureter's shortened submucosal course, the poorly developed trigone, and the abnormal morphology of the ureteral orifice
- Urinary continence
- Minimize overall procedural morbidity
- Options for ectopic ureter (2):
- Temporary end ureterostomy
- Consider if urgent diversion needed (e.g. a neonate with sepsis or with massive dilation associated with ectopic ureter may be best managed with a temporary end ureterostomy)
- Ureteroureterostomy, either low or proximal near the renal pelvis, in an end-to-side fashion
- When the upper pole of a duplex system associated with an ectopic ureter demonstrates function, preservation is typically recommended. Two reasonable options exist for this, including proximal ureteropyelostomy which excises most of the usually dilated upper pole ureter, or distal ureteroureterostomy, which permits drainage without any manipulation of the perirenal tissues.
- There are no data to support one over the other, and both are reasonable options.
- Common sheath reimplantation
- Upper pole partial nephrectomy (see below)
- Observation is only rarely suitable for a dilated ectopic ureter
- Options for ureterocele (5):
- Transurethral incision (TUI)
- Preferred method of incising the ureterocele is a transverse incision through the full thickness of the ureterocele wall using the cutting current
- Intra-vesical ureterocele more likely to be successfully treated than extra-vesical
- Intravesical ureteroceles have the highest likelihood of achieving all therapeutic goals with only the incision.
- Extravesical ureteroceles (spanning the bladder neck and urethra) are more likely to have persisting or new reflux and may require secondary surgery based on the presence of reflux
- Better prepares the patient for a secondary major surgery, if needed, by decompressing dilated ureters
- In general, it is not possible to predict how an individual might respond to TUI based on clinical parameters.
- Incidence of new reflux after TUI of a ureterocele ranges from 0-60%; may be dependent on the method used for incision.
- Persisting reflux into the upper or lower poles is typically an indication for ureterocele excision and reimplantation, but resolution has been reported
- Ureterocele excision and common sheath reimplantation or ureteroureterostomy
- The results of ureterocele excision and common sheath reimplantation are very good, although persisting reflux can be an issue in 5-10% of patients.
- Cecoureteroceles present a unique challenge in ureterocele excision and reimplantation in that the distal aspect of the ureterocele can create an obstructive flap-valve with voiding, acting like a windsock behind the urethra.
- In a cecoureterocele, the orifice of the affected ureter is within the bladder but the cavity of the ureterocele extends beyond the bladder neck into the urethra.
- Following open resection of a large ectopic ureterocele, high postvoid residuals may be a complication of prolapsing residual ureterocele tissue
- An alternative approach to ureterocele resection is marsupialization, in which the thin intravesical aspect is removed and the edge is sutured.
- Total reconstruction including upper pole nephrectomy with ureterocele excision and reimplantation of the lower pole ureter
- Definitive but an extensive operation performed with two incisions
- Observational with prophylactic antibiotics is a reasonable option in carefully selected patients (such as in the setting of no reflux and a draining upper pole associated with a ureterocele), to permit spontaneous resolution and no surgical intervention. Prophylactic antibiotics are recommended until resolution is demonstrated.
- Upper pole partial nephrectomy (see below)
- Upper Pole Partial Nephrectomy for Ectopic Ureter or Ureterocele
- Upper pole partial nephrectomy or heminephrectomy of a duplex system is preferred when there is:
- No function in the upper pole
- Concern about ineffective drainage following a drainage procedure (described above) because of massive dilation
- Primary concern is to avoid damaging the viable lower pole
- Postoperative evaluation is best performed with a Doppler sonogram to demonstrate normal blood flow to the lower pole, absence of a urinoma, and normal postoperative anatomy
- Usually successful in achieving definitive cure with ectopic ureter, as the residual stump is rarely problematic
- In ureteroceles in which lower pole reflux is present:
- Resolution may be seen in up to 20%
- New reflux may be seen in 15-50% of those where no reflux was present preoperatively
- Complications: loss of lower pole function, development of a postoperative upper pole urinoma
- Separation of the duplicated ureters during intravesical dissection should be discouraged because it can lead to injury of the common blood supply running longitudinally between the two ureters.
Summary of Clinical Decision Making
- Ectopic ureter
- Clinical decision making is much more straightforward for ectopic ureter than for ureteroceles and rests on whether to maintain the upper pole of a duplex system
- If the upper pole is maintained, then the surgical approach depends on the presence of reflux in the lower pole
- If lower pole reflux is present, a common sheath reimplantation or a lower pole reimplantation with distal upper to lower pole ureteroureterostomy is performed.
- If lower pole reflux is not present, either proximal or distal ureteroureterostomy is performed
- If reflux is present, the need for lower surgery to correct the reflux may influence the choice to avoid upper tract surgery.
- If the degree of function is ambiguous, a temporary end ureterostomy can be used to permit assessment out of the acute setting, particularly with a massively dilated ureter.
- If removal of the upper pole is chosen based on degree of dilation or the preference for removal of nonfunctioning, dysplastic tissue, only an upper pole nephrectomy is performed.
- As mentioned above, resolution of lower-pole reflux may be seen in up to 20%
- For the single-system ectopic ureter, preservation or removal is also based on degree of function and surgeon preference.
- Ureterocele in a duplex system
- The availability of endoscopic incision creates more options
- Although TUI is an operation, it is of a totally different nature than either an upper pole nephrectomy or a lower tract reconstruction. It is inappropriate to equate them as operations in a comparative manner.
- Because in some patients, significant lower pole reflux and upper tract dilation may be treated with a brief outpatient procedure with documented long-term results, it would seem reasonable to offer that TUI before moving directly to a more complex upper or lower tract reconstruction. Even if half of those patients may need subsequent surgery, it can be safely deferred until the child is older. There is also the further appeal of TUI in that it may make a subsequent surgical procedure less complex by decompressing a dilated upper pole ureter. Reimplantation may be much more effective and not require excisional tapering. This lessens overall morbidity, another goal of management.
- The appeal of TUI may be less in the older child with a massive upper pole in whom removal may be preferable and definitive surgery can be performed at diagnosis.
Other Ureteral Anomalies
- Bifid Ureters
- Ureteral duplication may be associated with ectopia or a ureterocele but is also compatible with a normally functioning renal system if both ureters enter orthotopically or if there is partial duplication
- A bifid renal pelvis that includes only a single ureter, but with confluence of the upper and lower ureters lower than the ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) constitutes partial duplication of the ureter or bifid ureter
- An increased incidence of ureterorenal pathology has been documented with duplication anomalies; when unilateral duplication is documented, the contralateral side should be assessed duplication
- Conditions routinely affecting a single system kidney are those that affect the lower pole, including UPJO and VUR; the upper pole is more likely affected by conditions resulting from abnormal ureteral formation, including ectopia and ureterocele
- Fibroepithelial Polyps
- May present with flank pain or hematuria or by incidental detection of hydronephrosis
- Most common site of attachment is at the UPJ, although they may originate from any part of the ureter.
- UPJ polyps are best treated with pyeloplasty; endoscopic resection may be sufficient
- Ureteroscopic removal of ureteral polyps is the recommended therapy away from the UPJ
- Ureteral triplication
- The most common form is all three ureters joining to terminate in a single bladder orifice
- Retrocaval Ureter (Circumcaval Ureter, Preureteral Vena Cava)
- A rare congenital anomaly
- Involves the right ureter
- Characteristic S-shaped deformity in which the ureter typically deviates medially behind (posterior to) the inferior vena cava, winding about and crossing in front of it from a medial to a lateral direction, to resume a normal course to the bladder.
- Occurs as a consequence of the persistence of the posterior cardinal veins (chapter 134 says subcardinal vein) during embryologic development;if the subcardinal vein in the lumbar portion fails to atrophy and becomes the primary right-sided vein, the ureter is trapped dorsal to it.
- Wikipedia: Most of the posterior cardinal veins regress, what remains of them forms the renal segment of the inferior vena cava and the common iliac veins. Later in the development stages, the posterior cardinal veins are replaced by the subcardinal and supracardinal veins.
- May manifest with symptoms of flank or abdominal pain or infection, or the disorder may be discovered incidentally
- Surgical correction involves ureteral division, with relocation and ureteroureteral or ureteropelvic reanastomosis, usually with excision or bypass of the retrocaval segment, which can be aperistaltic.
Questions
- In duplex kidney, which of the following are more likely associated with the upper vs. lower pole? Reflux, ureterocele, UPJO, ectopic ureteral orifice
- How is the presentation of ectopic ureter different in males or females?
- What is the most common site of insertion of ectopic ureter in the male?
- How does an infection related to ectopic ureter present compared to one related to ureterocele?
- What are the management options for ectopic ureter? Ureterocele?
Answers
- In duplex kidney, which of the following are more likely associated with the upper vs. lower pole? Reflux, ureterocele, UPJO, ectopic ureteral orifice
- How is the presentation of ectopic ureter different in males or females?
- What is the most common site of insertion of ectopic ureter in the male?
- How does an infection related to ectopic ureter present compared to one related to ureterocele?
- What are the management options for ectopic ureter? Ureterocele?
References
- Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Partin AW, Peters CA (eds): CAMPBELL-WALSH UROLOGY, ed 11. Philadelphia, Elsevier, 2015, chap 134