STONES: EPIDEMIOLOGY & PATHOGENESIS
Epidemiology of Urolithiasis
- Lifetime prevalence of kidney stone disease: ≈1%-15%, varies by age, gender, race, geographic location, and BMI
- Age: relatively uncommon age < 20 but peaks in incidence in the 40-60s
- Gender: upper urinary tract stones occur more commonly in males than females, but gender gap is narrowing
- Race: Whites have the highest incidence of upper tract stones compared with Asians, Hispanics, and African-Americans
- Geographic location: In the US, highest prevalence in the Southeast
- BMI, waist size, and weight gain are positively correlated with an increased risk for stone episodes
- Incidence of asymptomatic renal stones is ≈10% of screened populations
Physicochemistry and pathogenesis
- Urine must be supersaturated for stones to form; supersaturation alone is not sufficient for crystallization to occur in urine due to the presence of urinary inhibitors
- The state of saturation of the urine with respect to particular stone-forming salts indicates the stone-forming propensity of the urine. The state of saturation is determined by pH and the ionic strength of the major ions in solution.
- The solubility product refers to the point of saturation where dissolved and crystalline components in solution are in equilibrium. Addition of more crystals to the solution will result in precipitation of crystals. In this supersaturated urine (metastable state), crystallization can occur on preexisting crystals, but spontaneous crystallization occurs only when the concentration product exceeds the formation product. In the supersaturated state, the presence of inhibitors prevents or delays crystallization.
- The process by which nuclei form in pure solutions is called homogeneous nucleation.
- Heterogeneous nucleation occurs when microscopic impurities or other constituents in the urine promote nucleation by providing a surface on which the crystal components can grow.
- Known inhibitors of calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate crystallization (6) No More Bad Colicky Torturous Urolithiasis:
- Nephrocalcin
- Magnesium
- Inhibitory activity derived from its complexation with oxalate, which reduces ionic oxalate concentration and calcium oxalate supersaturation
- Bikunin
- Citrate
- Most important factor
- MOA:
- Complexes calcium, thereby lowering urinary saturation of calcium oxalate
- Inhibits spontaneous precipitation of calcium oxalate and agglomeration of calcium oxalate crystals
- Inhibits calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate crystal growth, with effect on calcium phosphate crystal growth more pronounced than on calcium oxalate crystal growth
- Prevents heterogeneous nucleation of calcium oxalate by monosodium urate
- Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein
- Most abundant protein in the urine
- Uropontin
- No known inhibitors affect uric acid crystallization
- Renal calculi consist of 2 components: crystalline and non-crystalline (matrix) components
- Crystalline
- Calcium is the most common component of urinary calculi
- Non-crystalline (matrix)
- Typically accounts for 2.5% of the weight of the stone.
- Matrix is a heterogenous mixture consisting of ≈65% protein. Other components include mucoproteins, carbohydrates, and urinary inhibitor
- In idiopathic calcium oxalate stone formers, Randall plaques, which are composed of calcium apatite, have been found to originate in the basement membrane of the thin loops of Henle. From there, they extend through the medullary interstitium to a subepithelial location, where they serve as an anchoring site for calcium oxalate stone formation.
Mineral metabolism
- Calcium
- 30-40% of dietary calcium is absorbed from the intestine, with most being absorbed in the small intestine and only ≈10% absorbed in the colon
- Absorption of calcium varies with calcium intake by a process of intestinal adaptation - at times of low calcium intake, fractional calcium absorption is enhanced; during high calcium intake, fractional calcium absorption is reduced
- Substances that complex with calcium, such as oxalate, citrate, phosphate, sulfate, and fatty acids, reduce the availability of calcium for absorption
- Calcium homeostasis
- PTH
- Secreted in response to low serum calcium
- Functions (3):
- Increases renal reabsorption of calcium and reduces reabsorption of phosphate from distal tubule (primary effect)
- Stimulates the enzyme 1α-hydroxylase in the proximal renal tubule which converts 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (calcifediol/calcidiol) to 1,25(OH)2D3 (calcitriol)
- This enzyme is also stimulated by hypophosphatemia
- The first step to synthesis of calcitriol involves the conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol in the skin to previtamin D3 and is promoted by sunlight. Previtamin D3 is hydroxylated in the liver, which is further hydroxylated in the proximal renal tubule to 1,25(OH)2D3.
- Increases calcium release from bone
- A population-based study found that serum PTH levels were positively correlated with serum uric acid levels§
- Calcitriol (1,25(OH)2D3)
- Active form of Vitamin D
- Functions (4):
- Most potent stimulator of intestinal calcium absorption
- Note PTH does not target intestine
- Increases renal reabsorption of calcium and phosphate
- Note PTH increases phosphate excretion
- Similar to PTH, vitamin D induces calcium reabsorption in the distal tubule
- Increases calcium release from bone
- Inhibits release of PTH
- Most potent stimulator of intestinal calcium absorption
- PTH
- Oxalate
- Only 6-14% of ingested oxalate is absorbed (compared to 30-40% of ingested calcium is absorbed)
- Oxalate absorption occurs throughout the intestinal tract, with about half or more occurring in the small intestine and half in the colon
- Factors that influence oxalate absorption (2):
- Oxalate-degrading bacteria
- Oxalobacter formigenes use oxalate as an energy source and consequently reduce intestinal oxalate absorption
- Presence of oxalate-binding cations such as calcium or magnesium
- Co-ingestion of calcium, magnesium, and oxalate-containing foods leads to formation of calcium oxalate complexes, which limits the availability of free oxalate ion for absorption
- Absorbed oxalate is nearly completely excreted in the urine
- Urinary oxalate is derived from both endogenous production in the liver (from ascorbic acid and glycine) and dietary sources.
- On average, half of urinary oxalate is derived from the diet, with the precise amount depending on the relative amount of ingested calcium and oxalate
- It is estimated that between 86-98% of oxalate is ultrafilterable. However, renal tubular handling of oxalate has not been clearly defined, although both secretion and reabsorption have been suspected.
- Urinary oxalate is derived from both endogenous production in the liver (from ascorbic acid and glycine) and dietary sources.
- Only 6-14% of ingested oxalate is absorbed (compared to 30-40% of ingested calcium is absorbed)
Classification of nephrolithiasis
- Calcium-containing stones
- Calcium oxalate (60%)
- Hydroxyapatite (20%)
- Brushite (2%)
- Non-calcium containing stones
- Uric acid (7%)
- Struvite (7%)
- Cystine (1-3%)
- Triamterene (<1%)
- Silica (<1%)
- 2,8-dihydroxyadenine (<1%)
Calcium stones
- Urinary calcium and oxalate are both important and equal contributors to calcium oxalate stone formation
- Hypercalcuria
- Most common abnormality identified in calcium stone formers
- Recall, hypercalcuria is the most common cause of microscopic hematuria in children
- Classification:
- Absorptive hypercalcuria
- Characterized by
- Normal serum calcium
- Normal or suppressed PTH
- Hypercalcuria
- Increased intestinal absorption of calcium results in a transient increase in serum calcium, which suppresses serum PTH and results in increased renal filtration of calcium, ultimately leading to hypercalcuria.
- Serum calcium level remains normal because the increase in intestinal absorption of calcium is matched by enhanced renal calcium excretion
- Calcium fasting and load tests can discriminate between the various types of absorptive hypercalcuria; however, routine performance of these tests is not required
- Absorptive hypercalciuria type I: increased absorption will occur regardless of the amount of calcium in the diet. Therefore, these subjects will demonstrate an increased urinary excretion of calcium on both the fasting and the loading specimens.
- Absorptive hypercalciuria type II: normal amount of urinary calcium excretion during calcium restriction, but will show elevations during their regular diet
- Characterized by
- Renal (leak) hypercalcuria
- Characterized by
- Normal serum calcium
- Elevated PTH
- High fasting urinary calcium levels
- Impaired renal reabsorption of calcium results in elevated urinary calcium levels leading to secondary hyperparathyroidism (elevated PTH).
- Other causes of secondary hyperparathyroidism: rickets, osteopenia, CKD
- Patients may have low or low/normal radial bone density due to secondary hyperparathyroidism
- Serum calcium levels remain normal because the renal loss of calcium is compensated by enhanced intestinal absorption of calcium and bone resorption as a result of increased secretion of PTH
- The elevated serum PTH and elevated fasting urinary calcium (except if absorptive hypercalciuria I) levels differentiate renal from absorptive hypercalciuria
- Characterized by
- Resorptive hypercalcuria
- Infrequent abnormality; most commonly associated with primary hyperparathyroidism
- Characterized by:
- Elevated serum calcium
- Elevated PTH
- Hypercalcuria
- Hypophosphatemia
- Excessive PTH secretion from a parathyroid adenoma results in excessive bone resorption and increased renal synthesis of 1,25(OH)2D3, which in turn enhances intestinal absorption of calcium. The net effect is elevated serum and urine calcium levels and reduced serum phosphorus levels.
- Recurrent calcium phosphate (100%) brushite stones are unusual and should raise suspicion for primary hyperparathyroidism (resorptive hypercalciuria)
- Mechanism: elevated PTH increases phosphate excretion
- Additional, rare causes of resorptive hypercalciuria include hypercalcemia of malignancy, sarcoidosis, thyrotoxicosis, and vitamin D toxicity. Many granulomatous diseases, including tuberculosis, histoplasmosis, leprosy, and silicosis, have been reported to produce hypercalcemia.
- The hypercalcemia in sarcoidosis is due to the production of 1,25(OH)2D3 from 1α-hydroxylase present in macrophages of the sarcoid granuloma
- Idiopathic (unclassified) hypercalcuria
- Often refers to unevaluated or unknown cause
- Patients may demonstrate hypercalcuria in all phases of the dietary calcium manipulation, but will not demonstrate serum abnormalities
- Malignancy-associated hypercalemia
- An assay for intact PTH can help distinguish patients with hyperparathyroidism from those with other causes of hypercalcuria. Tumours in patients with humoral hypercalcemia produce a PTH-related protein (PTHrP)
- Glucocorticoid-induced hypercalemia
- Absorptive hypercalcuria
- Hyperoxaluria
- Classification (4):
- Primary hyperoxaluria
- Due to rare autosomal recessive inherited disorders in glyoxylate metabolism, leading to preferential oxidative conversion of glyoxylate to oxalate, an end product of metabolism
- Enteric hyperoxaluria
- In patients with enteric hyperoxaluria, intestinal hyperabsorption of oxalate is the most significant risk factor leading to recurrent calculus formation
- Fat malabsorption results in increased intestinal oxalate absorption
- In fat malabsorption, saponification of fatty acids occurs with divalent cations such as calcium and magnesium, which reduces calcium available for complexation with oxalate thereby resulting in an increased amount of oxalate available for reabsorption.
- The poorly absorbed fatty acids and bile salts may increase colonic permeability to oxalate, further enhancing intestinal oxalate absorption
- Patients with enteric hyperoxaluria are more likely to form calcium oxalate stones, due to increased urinary excretion of oxalate and decreased inhibitory activity from hypocitraturia, secondary to chronic metabolic acidosis and hypomagnesuria.
- Malabsorption of any cause (chronic diarrheal states, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac sprue, or intestinal resection) can lead to increased intestinal absorption of oxalate and hyperoxaluria; as a result of intestinal fluid loss, patients will often exhibit dehydration, bicarbonate losses, low urine volume
- Hyperoxaluria has been described in both stone-forming and non-stone-forming patients who have undergone Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery, with urinary oxalate levels in some patients exceeding 100 mg/day
- Bariatric surgery patients typically develop enteric hyperoxaluria, which should be managed with calcium supplementation
- Iron deficiency is the most common cause of anemia following bariatric surgery, particularly in premenopausal women.
- Bariatric surgery patients typically develop enteric hyperoxaluria, which should be managed with calcium supplementation
- Chronic diarrheal syndromes promote intestinal loss of alkali and dehydration, resulting in metabolic acidosis and reduced urinary citrate levels.
- Chronic metabolic acidosis can lead to low urine pH, hypercalciuria, and hypocitraturia.
- Hyperoxaluria has been described in both stone-forming and non-stone-forming patients who have undergone Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery, with urinary oxalate levels in some patients exceeding 100 mg/day
- Fat malabsorption results in increased intestinal oxalate absorption
- Restricting oxalate is generally insufficient as the cause is not an overabundance of oxalate
- In patients with enteric hyperoxaluria, intestinal hyperabsorption of oxalate is the most significant risk factor leading to recurrent calculus formation
- Dietary hyperoxaluria
- Overindulgence in oxalate-rich foods such as (Oxalate Rich Chocolate, Pepper, Nuts): Okra, Rhubarb, Chocolate, Pepper, Nuts, Tea (black), cocoa, spinach, mustard greens, pokeweed, swiss chard, beets, berries, wheat germ, and soy crackers can result in hyperoxaluria in otherwise normal individuals.
- Compliance is difficult for regimens intending to eliminate all oxalate sources
- Severe calcium restriction may result in reduced intestinal binding of oxalate and increased intestinal oxalate absorption, hence calcium intake should be moderate, rather than restricted
- Increasing calcium intake, which may include supplements, specifically timed with meals, may reduce hyperoxaluria
- High substrate levels (vitamin C) can also cause hyperoxaluria; doses should be limited to 2 g/day
- Overindulgence in oxalate-rich foods such as (Oxalate Rich Chocolate, Pepper, Nuts): Okra, Rhubarb, Chocolate, Pepper, Nuts, Tea (black), cocoa, spinach, mustard greens, pokeweed, swiss chard, beets, berries, wheat germ, and soy crackers can result in hyperoxaluria in otherwise normal individuals.
- Idiopathic hyperoxaluria
- Hyperuricosuria
- May be associated with pure uric acid calculi or calcium oxalate calculi through heterogenous nucleation
- Patients with hyperuricosuric calcium nephrolithiasis who form calcium oxalate stones present with normal urinary pH and hyperuricosuria, accompanied sometimes by hypercalciuria
- In contrast, those with gouty diathesis, who can form either uric acid or calcium oxalate calculi, have a low fractional excretion of urate (that contributes to hyperuricemia) and low urinary pH (that leads to increased amount of undissociated uric acid)
- Causes:
- Increased dietary purine intake (most common cause)
- Gout
- Myeloproliferative and lymphoproliferative disorders
- Multiple myeloma
- Thalassemia
- Hemolytic disorders
- Pernicious anemia
- Hemoglobinopathies
- Secondary polycythemia
- Complete or partial hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT) deficiency
- Lesch-Nyhan syndrome is an inherited deficiency of the purine salvage enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase, which leads to the accumulation of hypoxanthine, which is ultimately converted to uric acid
- Overactivity of phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase
- Hereditary renal hypouricemia
- Renal tubular acidosis (RTA)
- RTA is a clinical syndrome characterized by metabolic acidosis
- Classified: acquired vs. inherited;
- Causes of acquired RTA A CASH POT
- Analgesic nephropathy
- Idiopathic hyperCalciuria
- Acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
- Sarcoidosis
- Hyperparathyroidism (primary)
- Pyelonephritis, recurrent
- Obstructive uropathy
- Transplant (renal)
- 3 types: type 1 (distal), type 2 (proximal), and type 4 (distal)
- Type 1 (distal) RTA
- Most common form of RTA and most commonly associated with kidney stones (up to 70% of adults with type 1 RTA have kidney stones)
- Characterized by (5):
- Hyperchloremic, non-anion gap metabolic acidosis
- Increased urinary pH (>6.0)
- Hypercalcuria
- Hypocitraturia
- Hypokalemia
- Due to impaired acid (H+, hydrogen is first element in periodic table so type 1 ) excretion into the urine in the presence of systemic acidosis, from dysfunction of the alpha-type intercalated cells, which secrete protons into the urine via an apical H+-ATPase
- Metabolic acidosis may cause a negative calcium balance as a result of impaired renal tubular reabsorption of calcium in the proximal tubule, leading to excessive renal loss of calcium. In addition, intestinal calcium absorption is diminished in patients with persistent acidosis. Slow dissolution of bone mineral can also be identified as calcium and phosphate act as buffering mechanisms to correct the acidosis. Chronic acidosis has been cited as a major factor in the genesis of bone disease.
- Patients with the incomplete form of distal RTA are not persistently acidemic despite their inability to lower urinary pH with an acid load. The diagnosis of incomplete distal RTA can be confirmed by inadequate urinary acidification after an ammonium chloride loading test.
- Potassium citrate therapy is able to correct the metabolic acidosis and hypokalemia
- Most common stone composition associated with distal RTA is calcium phosphate as a result of increased urinary pH, hypercalciuria, and hypocitraturia
- Type 2 (proximal) RTA
- Due to impaired bicarbonate (bi=2, type 2) reabsorption
- Proximal RTA is characterized by a defect in HCO3− reabsorption associated with initial high urine pH that normalizes as plasma HCO3– decreases and the amount of filtered HCO3– falls. With reduced capacity of the proximal tubule to reclaim filtered HCO3−, more HCO3− is delivered to the distal tubule, which has a limited capacity for bicarbonate reabsorption. Consequently, bicarbonaturia ensues, resulting in reduced net acid excretion and metabolic acidosis. As the filtered HCO3- load declines with progressive metabolic acidosis, less bicarbonate reaches the distal tubule until eventually the capacity of the distal tubule is sufficient to handle the load and no further bicarbonate is lost. At steady state, serum HCO3− is low (15 to 18 mEq/L) and urine pH is acidic (<5.5).
- Nephrolithiasis is uncommon in this disorder as urinary citrate levels are not decreased, in contrast to type 1 RTA
- Type 4 (distal) RTA
- Type 1 (distal) RTA
- Usually seen in patients with chronic renal damage (obstructive uropathy, interstitial renal disease, diabetic nephropathy, multicystic dysplasia)
- Pathophysiology results from impaired response to mineralocorticoid caused by damage to the cortical collecting duct
- Associated with hyperkalemia
- Nephrolithiasis is uncommon in this disorder
- Nephrocalcinosis
- Formation of diffuse deposits of calcium throughout the kidneys
- Usually occurs within the renal medulla but occasionally it has been found in the cortex or within both the medulla and the cortex
- Minute calcifications seen in early stages may not be visible
- Can give rise to renal colic and hydronephrosis from dislodged calcific foci
- Causes§
- Medulla
- Type 1 (distal) RTA
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Medullary sponge kidney
- Hypervitaminosis D
- Milk-alkali syndrome
- Sarcoidosis
- Hyper/hypothyroidism
- Other pathological hypercalcemic or hypercalciuric states
- Cushing syndrome
- Multiple myeloma
- Bartter syndrome
- Bone metastases
- Pyramids
- Hyperuricemia
- Infection (particularly renal tuberculosis)
- Sickle cell disease (leading to infarction and subsequent dystrophic calcification)
- Renal papillary necrosis
- Drugs
- Furosemide abuse
- Corticol COAG
- Corticol necrosis
- Oxalosis
- Alport syndrome
- Glomerulonephritis (chronic)
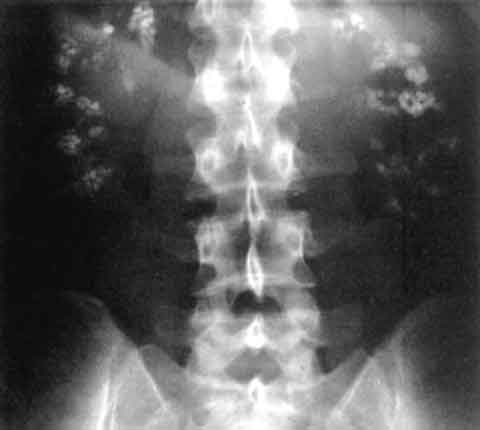
Plain film x-ray demonstrating bilateral diffuse calcium deposits in the kidneys
Source: Wikipedia
- Hypomagnesiuria
- Rare cause of nephrolithiasis
- Most common cause is inflammatory bowel disease associated with malabsorption
- Frequently associated with chronic thiazide therapy
- Magnesium complexes with oxalate and calcium salts, and therefore low magnesium levels result in reduced inhibitory activity. Low urinary magnesium is also associated with decreased urinary citrate levels
- Hypocitraturia
- Acid-base state is the primary determinant of urinary citrate excretion
- Metabolic acidosis reduces urinary citrate levels by augmenting citrate reabsorption and mitochondrial oxidation
- Metabolic alkalosis enhances citrate excretion
- Causes (4) DIRT:
- Chronic Diarrhea
- Idiopathic
- Type 1 (distal) RTA: laboratory hallmark is low urine citrate with an inappropriately high urine pH; Severe hypocitraturia should immediately raise suspicious for RTA.
- Thiazide-induced (side effects of thiazide therapy)
- Urine pH
- At low urine pH (<5.5), the undissociated form of uric acid predominates, leading to uric acid and/or calcium stone formation.
- Any disorder leading to low urine pH may predispose to stone formation.
- Calcium oxalate stones can form in low urine pH as a result of heterogeneous nucleation with uric acid crystals.
- Chronic metabolic acidosis can lead to low urine pH, hypercalciuria, and hypocitraturia.
- At low urine pH (<5.5), the undissociated form of uric acid predominates, leading to uric acid and/or calcium stone formation.
Uric acid stones
- Determinants of uric acid stone formation (3):
- Low urine pH (<5.5) (most important)
- Urine pH remains the most cost-effective means of screening for this condition and monitoring therapy.
- Low urine volume
- Hyperuricosuria
- Causes: congenital vs. acquired
- Congenital
- Disorders associated with uric acid stones involve renal tubular urate transport or uric acid metabolism, leading to hyperuricosuria
- Acquired:
- Diabetes
- Diabetic stone formers have a lower urine pH compared with non-diabetic stone formers due to insulin resistance
- In normal individuals, insulin stimulates ammoniagenesis in renal tubule cells by promoting gluconeogenesis from glutamine and by stimulating ammonium excretion by the proximal tubular sodium/hydrogen exchanger. Failure of the renal tubule cells to respond to insulin results in defective ammonia production and/or excretion, thereby leading to a reduction in urinary pH and uric acid stone formation.
- Diabetic stone formers are approximately 6x more likely to develop a uric acid stone.
- Uric acid stones are found in 34% of stone-forming patients with diabetes mellitus compared to 6% of non-diabetic stone formers
- Diabetic stone formers have a lower urine pH compared with non-diabetic stone formers due to insulin resistance
- Obesity
- Metabolic syndrome
- Tumour lysis syndrome
- Volume depletion
- High animal protein intake
- Chronic diarrhea
- Uricosuric drugs
- Idiopathic
- Diabetes
- All 11 conditions associated with hyperuricosuria listed above
Cystine stones
- Cystinuria
- An inherited autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations of SLC7A9 or SLC3A1
- Results in inadequate renal tubular reabsorption of the amino acids Cystine, Ornithine, Lysine, and Arginine (COLA), and also inadequate intestinal absorption of these amino acids
- Several factors determine the solubility of cystine, including cystine concentration, pH, ionic strength, and urinary macromolecules
- May be accompanied by other metabolic abnormalities
- Stones are considered poorly radioopaque on imaging§
- Sodium nitroprusside spot test will turn urine purple in the presence of cystine.
- Used for screening purposes to identify patients with cystine stone disease who are undergoing a 24 hour urine collection for evaluation.
Infection stones (magnesium ammonium phosphate)
- Struvite stones occur only in association with urinary infection by urea-splitting organisms.
- Urease hydrolyzes urea, forming ammonium and carbon dioxide, which increases urinary pH.
- Alkaline urine promotes supersaturation and precipitation of crystals of magnesium ammonium phosphate and carbonate apatite.
- Urease hydrolyzes urea, forming ammonium and carbon dioxide, which increases urinary pH.
- Most common urease-producing pathogens (4):
- Proteus (most common)
- Klebsiella
- Pseudomonas
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Some yeasts and mycoplasma species have the capacity to synthesize urease
- Although E. coli is a common cause of UTIs, only rare species of E. coli produce urease
- Pathogenesis
- Occur more often in females than males by a ratio of 2:1 because infection stones occur most commonly in those prone to frequent UTIs.
- Other populations at risk of recurrent infection include the diabetics, elderly, premature infants or congenital urinary tract malformation, urinary stasis as a result of urinary tract obstruction, urinary diversion, or neurologic disorders
- Spinal cord–injured patients are at particular risk for both infection and metabolic stones owing to neurogenic urinary tract dysfunction and hypercalciuria related to immobility
- Occur more often in females than males by a ratio of 2:1 because infection stones occur most commonly in those prone to frequent UTIs.
- Commonly produce staghorn stones; however, other crystals, including cystine, calcium oxalate monohydrate, and uric acid, can assume a staghorn configuration
- See Table 52-7
Other stones
- Matrix stones
- Rare
- Predominately composed (65%) of organic proteins, sugars, and glucosaminses, unlike other stones that have minimal organic material (2.5%)
- Among the proteins incorporated into the matrix substance are Tamm-Horsfall protein, nephrocalcin, a γ-carboxyglutamic acid–rich protein, renal lithostathine, albumin, glycosaminoglycans, free carbohydrates, and a mucoprotein called matrix substance A
- Most common predisposing factors: recurrent UTI by urea-splitting bacteria, previous stone formation, previous surgery due to urolithiasis and obstructive uropathy
- Challenging to diagnose preoperatively, as they can mimic upper tract collecting system soft-tissue masses and require a high index of suspicion
- Radiolucent on plain film x-ray
- Xanthine stones
- Result of an inherited disorder in xanthine dehydrogenase (XDH) or xanthine oxidase.
- Allopurinol, which inhibits XDH and is consequently used to treat hyperuricemia and hyperuricosuria, can, at high levels, predispose to xanthine stones. This side effect is distinctly uncommon
- Radiolucent on plain film x-ray
- 2,8-dihydroxyadenine stone
- Results from adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency, a rare autosomal recessive disorder
- Radiolucent on plain film x-ray
- Ammonium acid urate stones
- Infrequently seen in industrialized nations
- Associated with laxative abuse, recurrent UTI, recurrent uric acid stone formation, inflammatory bowel disease, and children with low-protein, low-phosphate diet resulting in primary bladder calculus
- Ammonium excretion is increased with starvation, dehydration, or consumption of acid-forming foods or toxins§
- Subjects who abuse laxatives are chronically dehydrated, resulting in intracellular acidosis. In addition, urinary sodium is low from sodium loss as a result of the laxatives. In this environment, urate preferentially complexes with the abundant ammonium rather than sodium and produces ammonium acid urate stones.
- Medication associated stones (12): Lotta Good Drugs Cause Calculi FIT TEST
- Laxatives
- Guaifenesin
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin C
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
- May be associated with the formation of calcium-based calculi, particularly calcium phosphate
- Furosemide
- Thiazides cause intracellular acidosis and subsequent hypocitraturia
- Indinavir
- MOA: protease inhibitor
- Used in patients with HIV/AIDS.
- Individuals taking indinavir on a regular basis are at high risk of producing indinavir stones because of the high urinary excretion and poor solubility of the drug at physiologic urinary pH.
- Now infrequently used, replaced with newer generation agents. Kidney stone formation has been associated with a number of newer anti-retroviral agents.
- Radiolucent on plain film and may not be seen on CT
- Topiramate
- Used to treat epilepsy and prevent migraines
- Creates a chronic intracellular acidosis resulting in a urinary milieu similar to distal RTA with hyperchloremic acidosis, high urine pH, extremely low urinary citrate, and hypercalciuria.
- Treatment may be potassium citrate or cessation of the medication if possible.
- Triamterene
- MOA: potassium-sparing diuretic
- Used for the treatment of hypertension
- Radiolucent
- Ephedrine
- Silicates
- TMP/SMX
Anatomic predisposition to stones
- Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction (UPJO)
- Correction of the UPJO does not prevent recurrent stones in most patients, emphasizing the role of underlying metabolic abnormalities in the etiology of renal calculi in patients with UPJO
- Horseshoe kidneys
- Although urinary stasis likely contributes to a propensity toward stone formation in patients with horseshoe kidneys, an underlying metabolic abnormality is required for stone formation to occur
- Caliceal Diverticula
- Medullary Sponge Kidney
- Congenital disorder
- Characterized by cystic dilatation of the collecting tubules in one or both kidneys, resulting in stasis of urine and may eventually lead to calculi deposits
- May independently cause both nephrocalcinosis (see above) and distal RTA with associated RTA metabolic abnormalities including hypercalciuria, hypocitraturia and defective urinary acidification
- Increased risk for kidney stones and UTI
- Imaging: hyperechoic papillae with clusters of small stones on ultrasound examination of the kidney or with an abdominal x-ray.
Questions
- List inhibitors of calcium oxalate formation.
- What are functions of PTH?
- What stimulates release of PTH?
- What are the functions of vitamin D?
- What is the most common metabolic abnormality found in stone formers?
- What are 4 different types of hypercalcuria and what would their blood work show?
- What are the 4 different types of hyperoxaluria?
- Why is intestinal malabsorption associated with hyperoxaluria?
- List 5 oxalate rich foods
- What is the most common cause of hyperuricosuria?
- List 6 causes of hyperuricosuria
- List 8 causes of acquired RTA
- What are the 3 different types of RTA, metabolic abnormality, and which is associated most commonly with stones?
- List 4 causes of hypocitraturia
- What are 2 lithogenic metabolic derangements associated with thiazide use?
- List 10 conditions associated with uric acid stones
- What are the main determinants of uric acid stone formation?
- What is the inheritance pattern associated with cysteine stones?
- Impaired reabsorption of which amino acids occurs in cystinuria?
- List 4 radiolucent stones
- Which metabolic abnormality is associated with excess vitamin C intake?
- Which type of stone is associated with laxative abuse?
- List 5 stone types that are formed from medications?
- List anatomic causes the predispose patients to stone formation
Answers
- List inhibitors of calcium oxalate formation.
- Nephrocalcin
- Magnesium
- Bikunin
- Citrate
- Tamms-Horsfall protein
- Uropontin
- What are functions of PTH?
- Stimulates reabsorption of calcium and excretion of phosphate in kidney
- Stimulates release of calcium from bone
- Stimulates to 1-alpha-hydroxylase enzyme to produce activated vitamin D
- What stimulates release of PTH?
- Hypocalcemia
- What are the functions of vitamin D?
- Increase intestinal calcium absorption (Note PTH does not target intestine)
- Increases renal reabsorption of calcium and phosphate (Note PTH increases phosphate excretion)
- Increases calcium release from bone
- Inhibits release of PTH
- What is the most common metabolic abnormality found in stone formers?
- Hypercalcuria
- What are 4 different types of hypercalcuria and what would their blood work show?
- Absorptive, normal serum calcium, normal/supressed PTH
- Renal leak, normal serum calcium, elevated PTH
- Resorptive, elevated serum calcium, elevated PTH
- Idiopathic
- What are the 4 different types of hyperoxaluria?
- Primary
- Enteric
- Dietary
- Idiopathic
- Why is intestinal malabsorption associated with hyperoxaluria?
- Intestinal malabsorption of fat results in saponification of fatty acids with calcium and other substrates that would otherwise bind oxalate; this results in increased oxalate absorption
- List 5 oxalate rich foods
- Okra, rhubarb, chocolate, pepper, nuts, beets, spinach
- What is the most common cause of hyperuricosuria?
- Increased dietary intake of purine
- List 6 causes of hyperuricosuria
- Gout
- Myeloproliferative disorder
- Multiple myeloma
- Thalassemia
- Hemolytic disorders
- Pernicious anemia
- Hemoglobinopathies
- Secondary polycythemia
- Complete or partial hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT) deficiency
- Overactivity of phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase
- Hereditary renal hypouricemia
- List 8 causes of acquired RTA
- Analgesic abuse
- Hypercalcemia
- ATN
- Sarcoidosis
- Hyperparathyroidism, primary
- Pyelonephritis, recurrent
- Obstructive uropathy
- Transplant, renal
- What are the 3 different types of RTA, metabolic abnormality, and which is associated most commonly with stones?
- Type 1: impaired H+ secretion, associated with stones
- Type 2: impaired bicarb reabsorption
- Type 4: renal failure
- List 4 causes of hypocitraturia
- Idiopathic
- Type 1 RTA
- Thiazide diuretics
- Chronic diarrhea
- What are 2 lithogenic metabolic derangements associated with thiazide use?
- Hypomagnesuria and hypocitraturia
- List 10 conditions associated with uric acid stones
- Chronic diarrhea
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Metabolic syndrome
- Tumour lysis syndrome
- Volume depletion
- High animal protein intake
- Uricosuric drugs
- All 11 conditions associated with hyperuricosuria listed above
- Idiopathic
- What are the main determinants of uric acid stone formation?
- Low urine pH (<5.5)
- Low urine volume
- Hyperuricosuria
- What is the inheritance pattern associated with cysteine stones?
- Autosomal dominant
- Impaired reabsorption of which amino acids occurs in cystinuria?
- Cystine, Ornithine, Lysine, Arginine
- List 4 radiolucent stones
- Uric acid
- Matrix
- Cystine
- Indinavir
- Trimaterene
- Xanthine
- 2,8-dihydroxyadenine stone
- Which metabolic abnormality is associated with excess vitamin C intake?
- Hyperoxaluria
- Which type of stone is associated with laxative abuse?
- Ammonium acid urate stones
- List 5 stone types that are formed from medications?
- Lotta Good Drugs Cause Calculi FIT TEST
- Laxatives
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin C
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
- Furosemide
- Indinavir
- Triamterene
- TMP/SMX
- Ephedrine
- Silicates
- Topiramate
- List anatomic causes the predispose patients to stone formation
- UPJO
- Horseshoe kidney
- Caliceal diverticula
- Medullary sponge kidney
References
- Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Partin AW, Peters CA (eds): CAMPBELL-WALSH UROLOGY, ed 11. Philadelphia, Elsevier, 2015, chap 51