Anatomy: Groin and Inguinal: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Urology4all (talk | contribs) Created page with "===Femoral Triangle=== *'''See [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/femoral-triangle-diagram radiopaedia figures]''' ====Borders==== *'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Roof: fascia lata (covers femoral sheath)''' **Fascia lata is continuous with external oblique aponeurosis superiorly[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aponeurosis_of_the_abdominal_external_oblique_muscle] *'''Floor: pectineus, iliopsoas, adductor longus muscles''' *'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Superior: inguinal lig..." |
Urology4all (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
===Femoral Triangle | == Groin == | ||
=== Vasculature === | |||
*'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Posterior to fascia lata</span>''' | |||
*'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Superficial vessels</span>''' | |||
**'''Supply the skin and subcutaneous tissue''' | |||
**'''Branches of the femoral artery (3)''' | |||
**#'''Superficial circumflex iliac artery''' | |||
**#*Smallest of the branches | |||
**#*Pierces through the fascia lata | |||
**#*'''Origin is usually lateral to the saphenous opening''' | |||
**#*Travels superolaterally, in the direction of the anterior superior iliac spine | |||
**#*Supplies | |||
**#**Region of the skin over the lateral third of the inguinal ligament and the iliac crest | |||
**#**Superficial fascia and superficial inguinal nodes along its course | |||
**#*Anastomoses with branches of the deep circumflex iliac, superior gluteal, and lateral circumflex femoral artery | |||
**#'''Superficial epigastric artery''' | |||
**#*Medial to the superficial circumflex iliac artery | |||
**#*Following a more vertical course; ascends anterior to the inguinal ligament up to the region just below the umbilicus | |||
**#*Typically originates from the anterior aspect of the femoral artery about 2–5 cm distal to the inguinal ligament | |||
**#**Often originates from a trunk that is shared with the superficial circumflex iliac artery | |||
**#*Supplies the skin, superficial fascia, and inguinal nodes in midinguinal area | |||
**#*Branches anastomose with those of the contralateral artery and with the inferior epigastric artery | |||
**#'''Superficial external pudendal artery''' | |||
**#*'''Medial origin on the femoral artery''' | |||
**#**Rarely it may originate from the profunda femoris artery | |||
**#*'''Medial route,''' coursing in the direction of the pubic symphysis where it traverses the spermatic cord in males and the round ligament in females | |||
**#*Supplies cutaneous blood flow to the inferior abdomen, the penis, and the scrotum in males and the labia majora in females | |||
**#*Anastomoses with branches of the internal pudendal artery | |||
**Anastomoses exist between the superficial and deep vessels | |||
*'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Deep vessels</span>''' | |||
**Supplies the muscles and fascia | |||
**'''Deep circumflex iliac''' | |||
***Branches off of the lateral aspect of the external iliac artery | |||
***Supplies the deep lateral groin | |||
**'''Inferior epigastric''' | |||
***Branch of the external iliac artery | |||
***Origin just medial to that of the deep circumflex iliac artery | |||
***Gives off two branches: the pubic and the external spermatic (or cremasteric) | |||
***Forms the lateral border of the inguinal (Hesselbach’s) triangle | |||
== Inguinal Lymph Nodes == | |||
*'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Classified as superficial vs. deep inguinal nodes</span>''' | |||
**'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Fascia lata of the thigh separates the superficial and deep inguinal nodes</span>''' | |||
*<span style="color:#ff0000">'''Superficial inguinal nodes'''</span> | |||
**'''Located deep to Camper’s fascia (also referred to as the superficial fascia) and superficial to the fascia lata (or deep fascia)''' | |||
**Arranged parallel to the inguinal ligament | |||
**Anatomic groups (5): | |||
**#Central nodes around the saphenofemoral junction | |||
**#Superolateral nodes around the superficial circumflex vein | |||
**#Inferolateral nodes around the lateral femoral cutaneous and superficial circumflex veins | |||
**#'''Superomedial nodes''' around the superficial external pudendal and superficial epigastric veins | |||
**##'''Drain the prepuce of the penis and the scrotum''' | |||
**#Inferomedial nodes around the greater saphenous vein | |||
*<span style="color:#ff0000">'''Deep inguinal nodes'''</span> | |||
**'''Lies deep to the fascia lata''' | |||
**'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Arranged parallel and primarily medial to the femoral vein in the femoral canal''' | |||
***Tend to be in close association with the femoral vein | |||
**Cluster of one to three lymph nodes | |||
***'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Fewer in number, compared to superficial inguinal nodes''' | |||
***'''Most cephalad of the deep inguinal nodes is the Node of Cloquet''' | |||
****Node of Cloquet is | |||
*****Almost always present | |||
*****Located in the femoral canal between the femoral vein and the lacunar ligament | |||
******Lacunar ligament connects the inguinal ligament to the pectineal ligament | |||
**Receives drainage from | |||
***Superficial group of lymph nodes | |||
***Deep lymphatics that run with the femoral artery | |||
***Glans of the penis and clitoris. | |||
==Femoral Triangle== | |||
*'''See [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/femoral-triangle-diagram radiopaedia figures]''' | *'''See [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/femoral-triangle-diagram radiopaedia figures]''' | ||
===Borders=== | |||
*'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Roof: fascia lata (covers femoral sheath)''' | *'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Roof: fascia lata (covers femoral sheath)''' | ||
**Fascia lata is continuous with external oblique aponeurosis superiorly[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aponeurosis_of_the_abdominal_external_oblique_muscle] | **Fascia lata is continuous with external oblique aponeurosis superiorly[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aponeurosis_of_the_abdominal_external_oblique_muscle] | ||
***Within the femoral sheath are the femoral artery and vein and the node of cloquet | |||
*'''Floor: pectineus, iliopsoas, adductor longus muscles''' | *'''Floor: pectineus, iliopsoas, adductor longus muscles''' | ||
*'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Superior: inguinal ligament (runs from anterior superior iliac spine to pubic tubercle)''' | *'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Superior: inguinal ligament (runs from anterior superior iliac spine to pubic tubercle)''' | ||
| Line 9: | Line 79: | ||
*'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Lateral: medial border of sartorius muscle''' | *'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Lateral: medial border of sartorius muscle''' | ||
*'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Medial: medial border of adductor longus muscle''' | *'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Medial: medial border of adductor longus muscle''' | ||
===Contents=== | |||
'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Lateral to medial: </span><span style="color:#0000ff">NAVEL</span>''' | '''<span style="color:#ff0000">Lateral to medial: </span><span style="color:#0000ff">NAVEL</span>''' | ||
*'''<span style="color:#0000ff">N</span><span style="color:#ff0000">erve</span>''' | *'''<span style="color:#0000ff">N</span><span style="color:#ff0000">erve</span>''' | ||
| Line 18: | Line 88: | ||
*'''<span style="color:#0000ff">L</span><span style="color:#ff0000">ymph nodes</span>''' | *'''<span style="color:#0000ff">L</span><span style="color:#ff0000">ymph nodes</span>''' | ||
[[File:Femoral triangle.png|thumb|Left femoral triangle; source: [[wikipedia:Femoral_triangle#/media/File:Gray549.png|Wikipedia]]|link=https://test.urologyschool.com/index.php/File:Femoral_triangle.png]] | [[File:Femoral triangle.png|thumb|Left femoral triangle; source: [[wikipedia:Femoral_triangle#/media/File:Gray549.png|Wikipedia]]|link=https://test.urologyschool.com/index.php/File:Femoral_triangle.png]] | ||
===Nerves=== | |||
*'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Femoral nerve</span>''' | *'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Femoral nerve</span>''' | ||
**'''Contains fibers originating from the L2–L4 spinal nerve roots''' | |||
**'''Lies deep to the iliacus fascia''' | **'''Lies deep to the iliacus fascia''' | ||
**'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Lateral to common femoral artery</span>''' | **'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Lateral to common femoral artery</span>''' | ||
***May at times be found between the artery and the vein | |||
**'''Functions''' | **'''Functions''' | ||
***'''Motor: innervates the | ***'''Motor: innervates the flexors of the hip and the extensors of the knee''' | ||
***'''Sensory: anterior thigh''' | ****'''Pectineus, quadriceps femoris, and sartorius muscles''' | ||
***'''Sensory: anterior thigh, anteromedial knee, medial leg, and medial foot''' | |||
**'''Should be preserved during inguinal dissection'''. | **'''Should be preserved during inguinal dissection'''. | ||
***Some of the sensory branches, however, are commonly sacrificed in the regional node dissection. | ***Some of the sensory branches, however, are commonly sacrificed in the regional node dissection. | ||
=== Vasculature === | |||
*'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Posterior to fascia lata</span>''' | *'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Posterior to fascia lata</span>''' | ||
*'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Common femoral artery</span>''' | *'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Common femoral artery</span>''' | ||
**Continuation of external iliac artery | **Continuation of external iliac artery | ||
| Line 45: | Line 120: | ||
**'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Medial to common femoral artery</span>''' | **'''<span style="color:#ff0000">Medial to common femoral artery</span>''' | ||
*Common femoral artery and common femoral vein are enclosed in femoral sheath[https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/femoral-artery] | *Common femoral artery and common femoral vein are enclosed in femoral sheath[https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/femoral-artery] | ||
==== | |||
== References == | |||
* Delman, Keith A., and Viraj A. Master. ''Malignancies of the Groin''. Springer International Publishing, 2018. | |||
* | |||
Revision as of 17:57, 17 July 2024
Groin
Vasculature
- Posterior to fascia lata
- Superficial vessels
- Supply the skin and subcutaneous tissue
- Branches of the femoral artery (3)
- Superficial circumflex iliac artery
- Smallest of the branches
- Pierces through the fascia lata
- Origin is usually lateral to the saphenous opening
- Travels superolaterally, in the direction of the anterior superior iliac spine
- Supplies
- Region of the skin over the lateral third of the inguinal ligament and the iliac crest
- Superficial fascia and superficial inguinal nodes along its course
- Anastomoses with branches of the deep circumflex iliac, superior gluteal, and lateral circumflex femoral artery
- Superficial epigastric artery
- Medial to the superficial circumflex iliac artery
- Following a more vertical course; ascends anterior to the inguinal ligament up to the region just below the umbilicus
- Typically originates from the anterior aspect of the femoral artery about 2–5 cm distal to the inguinal ligament
- Often originates from a trunk that is shared with the superficial circumflex iliac artery
- Supplies the skin, superficial fascia, and inguinal nodes in midinguinal area
- Branches anastomose with those of the contralateral artery and with the inferior epigastric artery
- Superficial external pudendal artery
- Medial origin on the femoral artery
- Rarely it may originate from the profunda femoris artery
- Medial route, coursing in the direction of the pubic symphysis where it traverses the spermatic cord in males and the round ligament in females
- Supplies cutaneous blood flow to the inferior abdomen, the penis, and the scrotum in males and the labia majora in females
- Anastomoses with branches of the internal pudendal artery
- Medial origin on the femoral artery
- Superficial circumflex iliac artery
- Anastomoses exist between the superficial and deep vessels
- Deep vessels
- Supplies the muscles and fascia
- Deep circumflex iliac
- Branches off of the lateral aspect of the external iliac artery
- Supplies the deep lateral groin
- Inferior epigastric
- Branch of the external iliac artery
- Origin just medial to that of the deep circumflex iliac artery
- Gives off two branches: the pubic and the external spermatic (or cremasteric)
- Forms the lateral border of the inguinal (Hesselbach’s) triangle
Inguinal Lymph Nodes
- Classified as superficial vs. deep inguinal nodes
- Fascia lata of the thigh separates the superficial and deep inguinal nodes
- Superficial inguinal nodes
- Located deep to Camper’s fascia (also referred to as the superficial fascia) and superficial to the fascia lata (or deep fascia)
- Arranged parallel to the inguinal ligament
- Anatomic groups (5):
- Central nodes around the saphenofemoral junction
- Superolateral nodes around the superficial circumflex vein
- Inferolateral nodes around the lateral femoral cutaneous and superficial circumflex veins
- Superomedial nodes around the superficial external pudendal and superficial epigastric veins
- Drain the prepuce of the penis and the scrotum
- Inferomedial nodes around the greater saphenous vein
- Deep inguinal nodes
- Lies deep to the fascia lata
- Arranged parallel and primarily medial to the femoral vein in the femoral canal
- Tend to be in close association with the femoral vein
- Cluster of one to three lymph nodes
- Fewer in number, compared to superficial inguinal nodes
- Most cephalad of the deep inguinal nodes is the Node of Cloquet
- Node of Cloquet is
- Almost always present
- Located in the femoral canal between the femoral vein and the lacunar ligament
- Lacunar ligament connects the inguinal ligament to the pectineal ligament
- Node of Cloquet is
- Receives drainage from
- Superficial group of lymph nodes
- Deep lymphatics that run with the femoral artery
- Glans of the penis and clitoris.
Femoral Triangle
Borders
- Roof: fascia lata (covers femoral sheath)
- Fascia lata is continuous with external oblique aponeurosis superiorly[1]
- Within the femoral sheath are the femoral artery and vein and the node of cloquet
- Fascia lata is continuous with external oblique aponeurosis superiorly[1]
- Floor: pectineus, iliopsoas, adductor longus muscles
- Superior: inguinal ligament (runs from anterior superior iliac spine to pubic tubercle)
- Inguinal ligament is the portion of the external oblique aponeurosis which extends between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic tubercle as a thick band, folded inward[2]
- Lateral: medial border of sartorius muscle
- Medial: medial border of adductor longus muscle
Contents
Lateral to medial: NAVEL
- Nerve
- Artery
- Vein
- Empty space
- Allows the veins and lymph vessels to distend to accommodate different levels of flow
- Lymph nodes
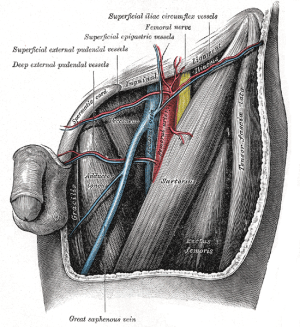
Nerves
- Femoral nerve
- Contains fibers originating from the L2–L4 spinal nerve roots
- Lies deep to the iliacus fascia
- Lateral to common femoral artery
- May at times be found between the artery and the vein
- Functions
- Motor: innervates the flexors of the hip and the extensors of the knee
- Pectineus, quadriceps femoris, and sartorius muscles
- Sensory: anterior thigh, anteromedial knee, medial leg, and medial foot
- Motor: innervates the flexors of the hip and the extensors of the knee
- Should be preserved during inguinal dissection.
- Some of the sensory branches, however, are commonly sacrificed in the regional node dissection.
Vasculature
- Posterior to fascia lata
- Common femoral artery
- Continuation of external iliac artery
- External iliac artery above inguinal ligament, common femoral artery below inguinal ligament
- Gives off a branch called deep (profunda) femoral artery and continues as superficial femoral artery[3]
- Blood supply to the skin of the inguinal region is from branches of the common femoral artery.
- Complete inguinal dissection necessitates ligation of these branches.
- Viability of the skin flaps raised during the dissection depends on anastomotic vessels in the superficial fatty layer of the Camper fascia
- A transverse skin incision least compromises blood supply to the skin.
- Complete inguinal dissection necessitates ligation of these branches.
- Medial to femoral nerve
- Just medial to the midpoint of the inguinal ligament in the inguinal crease region[4]
- Continuation of external iliac artery
- Common femoral vein
- Deep femoral vein and Great saphenous vein (also known as long saphenous vein) empty into the common femoral vein
- Great saphenous vein approaches common femoral vein medially
- Deep femoral vein approaches common femoral vein laterally
- Medial to common femoral artery
- Deep femoral vein and Great saphenous vein (also known as long saphenous vein) empty into the common femoral vein
- Common femoral artery and common femoral vein are enclosed in femoral sheath[5]
References
- Delman, Keith A., and Viraj A. Master. Malignancies of the Groin. Springer International Publishing, 2018.